Toward the discovery of vaccine adjuvants: coupling in silico screening and in vitro analysis of antagonist binding to human and mouse CCR4 receptors
- PMID: 20011659
- PMCID: PMC2787246
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008084
Toward the discovery of vaccine adjuvants: coupling in silico screening and in vitro analysis of antagonist binding to human and mouse CCR4 receptors
Abstract
Background: Adjuvants enhance or modify an immune response that is made to an antigen. An antagonist of the chemokine CCR4 receptor can display adjuvant-like properties by diminishing the ability of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells (Tregs) to down-regulate immune responses.
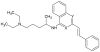
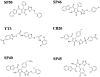
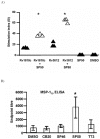
Methodology: Here, we have used protein modelling to create a plausible chemokine receptor model with the aim of using virtual screening to identify potential small molecule chemokine antagonists. A combination of homology modelling and molecular docking was used to create a model of the CCR4 receptor in order to investigate potential lead compounds that display antagonistic properties. Three-dimensional structure-based virtual screening of the CCR4 receptor identified 116 small molecules that were calculated to have a high affinity for the receptor; these were tested experimentally for CCR4 antagonism. Fifteen of these small molecules were shown to inhibit specifically CCR4-mediated cell migration, including that of CCR4(+) Tregs.
Significance: Our CCR4 antagonists act as adjuvants augmenting human T cell proliferation in an in vitro immune response model and compound SP50 increases T cell and antibody responses in vivo when combined with vaccine antigens of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Plasmodium yoelii in mice.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Medzhitov R, Janeway CA., Jr Innate immunity: impact on the adaptive immune response. Curr Opin Immunol. 1997;9:4–9. - PubMed
-
- Christopoulos A, Kenakin TG. protein-coupled receptor allosterism and complexing. Pharmacol Rev. 2002;54:323–374. - PubMed
-
- Bissantz C. Conformational changes of G protein-coupled receptors during their activation by agonist binding. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2003;23:123–153. - PubMed
-
- Luster AD. Chemokines–chemotactic cytokines that mediate inflammation. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:436–445. - PubMed
-
- Locati M, Murphy PM. Chemokines and chemokine receptors: biology and clinical relevance in inflammation and AIDS. Annu Rev Med. 1999;50:425–440. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

