ActRIIA and BMPRII Type II BMP receptor subunits selectively required for Smad4-independent BMP7-evoked chemotaxis
- PMID: 20011660
- PMCID: PMC2788225
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008198
ActRIIA and BMPRII Type II BMP receptor subunits selectively required for Smad4-independent BMP7-evoked chemotaxis
Abstract
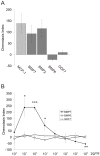
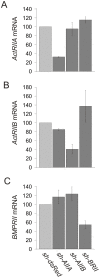
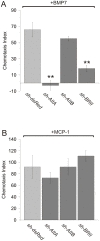
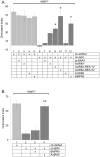
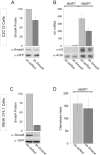
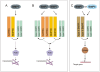
Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-evoked reorientation and chemotaxis of cells occurs with rapid onset and involves events local to the cell membrane. The signaling pathways underlying these rapid processes likely diverge from those mediating classical transcriptional responses to BMPs but it remains unclear how BMP receptors are utilized to generate distinct intracellular mechanisms. We show that BMP7-evoked chemotaxis of monocytic cells depends on the activity of canonical type II BMP receptors. Although the three canonical type II BMP receptors are expressed in monocytic cells, inhibition of receptor subunit expression by RNAi reveals that ActRIIA and BMPRII, but not ActRIIB, are each essential for BMP7-evoked chemotaxis but not required individually for BMP-mediated induction. Furthermore, the chemotactic response to BMP7 does not involve canonical Smad4-dependent signaling but acts through PI3K-dependent signaling, illustrating selective activation of distinct intracellular events through differential engagement of receptors. We suggest a model of a BMP receptor complex in which the coordinated activity of ActRIIA and BMPRII receptor subunits selectively mediates the chemotactic response to BMP7.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Inductive specification and axonal orientation of spinal neurons mediated by divergent bone morphogenetic protein signaling pathways.Neural Dev. 2011 Nov 15;6:36. doi: 10.1186/1749-8104-6-36. Neural Dev. 2011. PMID: 22085733 Free PMC article.
-
Structural distinctions in BMPs underlie divergent signaling in spinal neurons.Neural Dev. 2012 May 4;7:16. doi: 10.1186/1749-8104-7-16. Neural Dev. 2012. PMID: 22559862 Free PMC article.
-
Chemotropic signaling by BMP7 requires selective interaction at a key residue in ActRIIA.Biol Open. 2019 Jul 16;8(7):bio042283. doi: 10.1242/bio.042283. Biol Open. 2019. PMID: 31208997 Free PMC article.
-
Bone morphogenetic proteins.Growth Factors. 2004 Dec;22(4):233-41. doi: 10.1080/08977190412331279890. Growth Factors. 2004. PMID: 15621726 Review.
-
Signal transduction pathway through activin receptors as a therapeutic target of musculoskeletal diseases and cancer.Endocr J. 2008 Mar;55(1):11-21. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.kr-110. Epub 2007 Sep 14. Endocr J. 2008. PMID: 17878607 Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of a novel class of benzimidazoles as highly effective agonists of bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) receptor signaling.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 15;12(1):12146. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-16394-x. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35840622 Free PMC article.
-
SMAD-PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway mediates BMP-7 polarization of monocytes into M2 macrophages.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 20;8(12):e84009. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084009. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24376781 Free PMC article.
-
BMP2-induced chemotaxis requires PI3K p55γ/p110α-dependent phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-triphosphate production and LL5β recruitment at the cytocortex.BMC Biol. 2014 May 30;12:43. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-12-43. BMC Biol. 2014. PMID: 24885555 Free PMC article.
-
Blockade of bone morphogenetic protein signaling potentiates the pro-inflammatory phenotype induced by interleukin-17 and tumor necrosis factor-α combination in rheumatoid synoviocytes.Arthritis Res Ther. 2015 Jul 28;17(1):192. doi: 10.1186/s13075-015-0710-6. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 26215036 Free PMC article.
-
Inductive specification and axonal orientation of spinal neurons mediated by divergent bone morphogenetic protein signaling pathways.Neural Dev. 2011 Nov 15;6:36. doi: 10.1186/1749-8104-6-36. Neural Dev. 2011. PMID: 22085733 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sanchez-Camacho C, Rodriguez J, Ruiz JM, Trousse F, Bovolenta P. Morphogens as growth cone signalling molecules. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2005;49:242–252. - PubMed
-
- Charron F, Tessier-Lavigne M. Novel brain wiring functions for classical morphogens: a role as graded positional cues in axon guidance. Development. 2005;132:2251–2262. - PubMed
-
- Liu A, Niswander LA. Bone morphogenetic protein signalling and vertebrate nervous system development. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005;6:945–954. - PubMed
-
- Derynck R, Zhang YE. Smad-dependent and Smad-independent pathways in TGF-beta family signalling. Nature. 2003;425:577–584. - PubMed
-
- Shi Y, Massague J. Mechanisms of TGF-beta signaling from cell membrane to the nucleus. Cell. 2003;113:685–700. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

