Multiple cavitating nodules in a renal transplant recipient
- PMID: 20011727
- PMCID: PMC2807794
- DOI: 10.1155/2009/521548
Multiple cavitating nodules in a renal transplant recipient
Abstract
Pulmonary nodules are common following solid organ transplantation and vary in etiology. Nodules with central cavitation are most likely to be of infectious origin in the post-transplant population. A novel presentation of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder manifesting as multiple cavitating pulmonary nodules is described. The patient, a 45-year-old female renal transplant recipient, presented with constitutional symptoms and a chest x-ray showing multiple bilateral cavitating lesions. A computed tomography scan confirmed innumerable, randomly dispersed, cavitating nodules in the lung parenchyma. Multiple large hypodense lesions were identified in the liver and spleen. The appearance of the native and transplanted kidneys was normal. A liver biopsy identified an Epstein- Barr virus-negative, diffuse, large B cell lymphoma. Repeat imaging after treatment with a cyclophosphamide, hydroxydaunorubicin, oncovin and prednisone/prednisolone regimen demonstrated dramatic resolution of all lesions. The present case represents a unique radiographic presentation of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder not previously reported in the literature.
Les nodules pulmonaires sont courants après la greffe d’un organe solide, et leur étiologie varie. Les nodules dotés d’une cavité centrale sont plus susceptibles d’être d’origine infectieuse chez la population greffée. On décrit un cas de nouvelle présentation d’un trouble lymphoprolifératif après une greffe, se manifestant par de multiples nodules pulmonaires cavitaires. La patiente, une femme de 45 ans greffée du rein, a consulté en raison de symptômes constitutionnels et d’une radiographie pulmonaire révélant de multiples lésions cavitaires bilatérales. Une tomodensitométrie a confirmé la présence d’innombrables nodules cavitaires répartis aléatoirement dans le parenchyme pulmonaire. On a dépisté de grosses lésions hypodenses multiples dans le foie et la rate. L’apparence du rein indigène et du rein greffé était normale. Une biopsie rénale a permis de repérer un important lymphome à grosses cellules B diffus, négatif au virus d’Epstein-Barr. La reprise de l’imagerie, après le traitement à la cyclophosphamide, à l’hydroxydaunorubicine, à l’oncovine et à la prednisone et prednisolone, a révélé une résolution remarquable de toutes les lésions. Le présent cas constitue une présentation radiographique unique de trouble lymphoprolifératif après une greffe, jamais publiée auparavant.
Figures
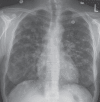
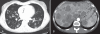
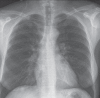
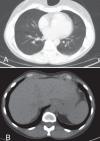
Similar articles
-
Posttransplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder Manifesting as Intestinal Epstein-Barr Virus-Positive Anaplastic Large-Cell Lymphoma in an Adult Renal Transplant Recipient.Exp Clin Transplant. 2016 Nov;14(Suppl 3):64-66. Exp Clin Transplant. 2016. PMID: 27805515
-
Application of contrast-enhanced ultrasonography in the diagnosis of post-kidney transplant lymphoproliferative disorder in native kidney- a case report.BMC Cancer. 2019 Nov 21;19(1):1135. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6355-0. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31752767 Free PMC article.
-
Posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder with lung involvement in a renal transplant recipient.Exp Clin Transplant. 2011 Dec;9(6):425-8. Exp Clin Transplant. 2011. PMID: 22142053
-
Tuberculosis combined with Burkitt lymphoma in a kidney transplant recipient: A case report and literature review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 May 5;102(18):e33671. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000033671. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37144990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-transplant multiple myeloma in a pediatric renal transplant patient.Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2006 Aug;47(2):218-23. doi: 10.1002/pbc.20482. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16086426 Review.
Cited by
-
Ultrasound for monitoring different stages of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder in a transplanted kidney: A case report and review of the literature.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Feb 23;103(8):e36206. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036206. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38394510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathologic review of cystic and cavitary lung diseases.Korean J Pathol. 2012 Oct;46(5):407-14. doi: 10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.5.407. Epub 2012 Oct 25. Korean J Pathol. 2012. PMID: 23136566 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dodd GD, III, Ledesma-Medina J, Baron RL, Fuhrman CR. Post transplant lymphoproliferative disorder: Intrathoracic manifestations. Radiology. 1992;184:65–9. - PubMed
-
- Caillard S, Lelong C, Pessione F, Moulin B, French PTLD Working Group Post transplant lymphoproliferative disorders occurring after renal transplantation in adults: Report of 230 cases from the French registry. Am J Transplant. 2006;6:2735–42. - PubMed
-
- Capello D, Rossi D, Gaidano G. Post transplant lymphoproliferative disorders: Molecular basis of disease histogenesis and pathogenesis. Hematol Oncol. 2005;23:61–7. - PubMed
-
- Opelz G, Dohler B. Lymphomas after solid organ transplantation: A collaborative transplant study report. Am J Transplant. 2004;2:222. - PubMed
-
- Burney K, Bradley M, Buckley A, Lyburn I, Rye A, Hopkins R. Post transplant lymphoproliferative disorder: A pictorial review. Austral Radiol. 2006;50:412–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

