Very preterm birth is a risk factor for increased systolic blood pressure at a young adult age
- PMID: 20012998
- PMCID: PMC2810359
- DOI: 10.1007/s00467-009-1373-9
Very preterm birth is a risk factor for increased systolic blood pressure at a young adult age
Abstract
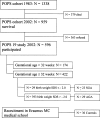
Children born very prematurely who show intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR) are suggested to be at risk of developing high blood pressure as adults. Renal function may already be impaired by young adult age. To study whether very preterm birth affects blood pressure in young adults, we measured 24-h ambulatory blood pressure (Spacelabs 90207 device) and renin concentration in 50 very premature individuals (<32 weeks of gestation), either small (SGA) or appropriate (AGA) for gestational age (21 SGA, 29 AGA), and 30 full-term controls who all were aged 20 years at time of measurement. The mean (standard deviation) daytime systolic blood pressure in SGA and AGA prematurely born individuals, respectively, was 122.7 (8.7) and 123.1 (8.5) mmHg. These values were, respectively, 3.6 mmHg [95% confidence interval (CI) -0.9 to 8.0] and 4.2 mmHg (95% CI 0.4-8.0) higher than in controls [119.6 (7.6)]. Daytime diastolic blood pressure and nighttime blood pressure did not differ between groups. We conclude that individuals born very preterm have higher daytime systolic blood pressure and higher risk of hypertension at a young adult age.
Similar articles
-
Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring and renal functions in term small-for-gestational age children.Pediatr Nephrol. 2011 Jan;26(1):119-26. doi: 10.1007/s00467-010-1646-3. Epub 2010 Oct 2. Pediatr Nephrol. 2011. PMID: 20886357
-
Increased blood pressure but normal renal function in adult women born preterm.Pediatr Nephrol. 2000 Dec;15(3-4):215-20. doi: 10.1007/s004670000473. Pediatr Nephrol. 2000. PMID: 11149114
-
Effect of birth weight on life-course blood pressure levels among children born premature: the Cardiovascular Risk in Young Finns Study.J Hypertens. 2015 Aug;33(8):1542-8. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000000612. J Hypertens. 2015. PMID: 26136063
-
Blood Pressure in Young Adults Born at Very Low Birth Weight: Adults Born Preterm International Collaboration.Hypertension. 2016 Oct;68(4):880-7. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.116.08167. Epub 2016 Aug 29. Hypertension. 2016. PMID: 27572149 Review.
-
Association of Intrauterine Growth Restriction and Small for Gestational Age Status With Childhood Cognitive Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JAMA Pediatr. 2020 Aug 1;174(8):772-781. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.1097. JAMA Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32453414 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Low nephron number and its clinical consequences.Rambam Maimonides Med J. 2011 Oct 31;2(4):e0061. doi: 10.5041/RMMJ.10061. Print 2011 Oct. Rambam Maimonides Med J. 2011. PMID: 23908819 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of preterm birth on blood pressure in later life: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Family Med Prim Care. 2023 Nov;12(11):2805-2826. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_684_23. Epub 2023 Nov 21. J Family Med Prim Care. 2023. PMID: 38186804 Free PMC article.
-
Intrauterine growth restriction, preterm birth and risk of end-stage renal disease during the first 50 years of life.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2020 Jul 1;35(7):1157-1163. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfaa001. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2020. PMID: 32040151 Free PMC article.
-
Paternal DNA Methylation May Be Associated With Gestational Age at Birth.Epigenet Insights. 2020 Sep 10;13:2516865720930701. doi: 10.1177/2516865720930701. eCollection 2020. Epigenet Insights. 2020. PMID: 32964196 Free PMC article.
-
Baroreflex sensitivity and blood pressure in premature infants - dependence on gestational age, postnatal age and sex.Physiol Res. 2021 Dec 31;70(S3):S349-S356. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934829. Physiol Res. 2021. PMID: 35099253 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous