The effects of infusions of CART 55-102 into the basolateral amygdala on amphetamine-induced conditioned place preference in rats
- PMID: 20013112
- PMCID: PMC4861404
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-009-1748-4
The effects of infusions of CART 55-102 into the basolateral amygdala on amphetamine-induced conditioned place preference in rats
Abstract
Rationale: The affective aspects of D: -amphetamine (AMPH) may be mediated, in part, by cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART) peptides in the basolateral amygdala (BLA). The formation of context-drug associations produces either conditioned place preference (CPP) or conditioned place aversion (CPA).
Objectives: The aim of the present study was to determine whether intra-BLA infusions of CART 55-102 are either rewarding or aversive and modulate AMPH reward.
Materials and methods: Rats were implanted with bilateral cannulae in the BLA, were subjected to place conditioning, and were tested for CPP or CPA. Rats were conditioned with either intra-BLA infusions of artificial cerebral spinal fluid or one of three dose of CART 55-102 (1, 2, or 4 microg/side), intra-BLA infusions of a subrewarding dose of CART 55-102 (1 microg/side) plus injections of a subrewarding dose of AMPH (0.1 mg/kg, i.p.), or intra-BLA infusions of an aversive dose of CART 55-102 (4 microg/side) plus injections of a rewarding dose of AMPH (1.0 mg/kg, i.p.).
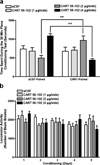
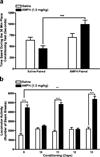
Results: Intra-BLA infusions of 2 microg/side CART 55-102 produced CPP, 4 microg/side produced CPA, and 1 microg/side produced neither CPP nor CPA. Intra-BLA infusions of a subrewarding dose of CART 55-102 (1 microg/side) plus injections of a subrewarding dose of AMPH (0.1 mg/kg, i.p.) produced CPP. Intra-BLA infusions of an aversive dose of CART 55-102 (4 microg/side) plus injections of a rewarding dose of AMPH (1.0 mg/kg, i.p.) produced neither CPP nor CPA.
Conclusions: Both the affective properties of intra-BLA CART 55-102 and its ability to either facilitate or block AMPH reward are dose dependent.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
The effect of microinjection of CART 55-102 into the nucleus accumbens shell on morphine-induced conditioned place preference in rats: Involvement of the NMDA receptor.Peptides. 2020 Jul;129:170319. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2020.170319. Epub 2020 Apr 23. Peptides. 2020. PMID: 32335205
-
Effect of amphetamine place conditioning on excitatory synaptic events in the basolateral amygdala ex vivo.Neuroscience. 2012 Mar 29;206:7-16. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.01.015. Epub 2012 Jan 18. Neuroscience. 2012. PMID: 22280974 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral effects of psychomotor stimulant infusions into amygdaloid nuclei.Neuropsychopharmacology. 1999 Jun;20(6):591-602. doi: 10.1016/S0893-133X(98)00083-9. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1999. PMID: 10327428
-
The CART (cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript) system in appetite and drug addiction.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007 Feb;320(2):499-506. doi: 10.1124/jpet.105.091512. Epub 2006 Jul 13. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007. PMID: 16840648 Review.
-
Conditioned Place Preference.In: Buccafusco JJ, editor. Methods of Behavior Analysis in Neuroscience. 2nd edition. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2009. Chapter 4. In: Buccafusco JJ, editor. Methods of Behavior Analysis in Neuroscience. 2nd edition. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2009. Chapter 4. PMID: 21204336 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Signaling in rat brainstem via Gpr160 is required for the anorexigenic and antidipsogenic actions of cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript peptide.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2021 Mar 1;320(3):R236-R249. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00096.2020. Epub 2020 Nov 18. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33206556 Free PMC article.
-
Cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART) signaling within the paraventricular thalamus modulates cocaine-seeking behaviour.PLoS One. 2010 Sep 23;5(9):e12980. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012980. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20886038 Free PMC article.
-
Intraperitoneal Administration of CART 55-102 Inhibits Psychostimulant-Induced Locomotion.J Drug Alcohol Res. 2012 Jan 1;1:235601. doi: 10.4303/jdar/235601. J Drug Alcohol Res. 2012. PMID: 23705073 Free PMC article.
-
Increased intake of energy-dense diet and negative energy balance in a mouse model of chronic psychosocial defeat.Eur J Nutr. 2018 Jun;57(4):1485-1498. doi: 10.1007/s00394-017-1434-y. Epub 2017 Mar 17. Eur J Nutr. 2018. PMID: 28314964
-
CART Peptides and Drugs of Abuse: A Review of Recent Progress.J Drug Alcohol Res. 2016;5:235984. doi: 10.4303/jdar/235984. Epub 2016 Jun 28. J Drug Alcohol Res. 2016. PMID: 29238623 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asan E. Ultrastructural features of tyrosine-hydroxylase-immunoreactive afferents and their targets in the rat amygdala. Cell Tissue Res. 1997;288:449–469. - PubMed
-
- Asan E. The catecholaminergic innervation of the rat amygdala. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 1998;142:1–118. - PubMed
-
- Bardo MT, Bevins RA. Conditioned place preference: what does it add to our preclinical understanding of drug reward? Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2000;153:31–43. - PubMed
-
- Cahill L, McGaugh JL. Mechanisms of emotional arousal and lasting declarative memory. Trends Neurosci. 1998;21:294–299. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

