Cartilage degeneration is associated with augmented chemically-induced joint pain in rats: a pilot study
- PMID: 20013164
- PMCID: PMC2853651
- DOI: 10.1007/s11999-009-1193-z
Cartilage degeneration is associated with augmented chemically-induced joint pain in rats: a pilot study
Abstract
Background: Osteoarthritis arising from cartilage degeneration is the most common cause of joint pain. However, the relationship between joint pain and cartilage degeneration is not well understood.
Questions/purposes: We asked whether the inflammatory mediators participate in the joint pain in the presence of cartilage degeneration.
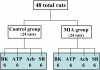
Methods: We observed electromyographic responses of hindlimb flexors to four inflammatory mediators (bradykinin, ATP, acetylcholine, and serotonin) injected in normal rat knees and in those with monosodium iodoacetate (MIA)-induced arthritis.
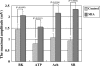
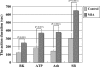
Results: Joint cartilage of all the rats with MIA-induced arthritis histologically showed severe degeneration. We observed greater magnitude and longer duration responses in the MIA-induced arthritis than normal joints with all four mediators.
Conclusions: The data suggested nociceptors in osteoarthritic joints are more sensitive to inflammatory mediators than in normal joints. Such nociceptive sensitization to inflammatory mediators may participate in the joint pain in osteoarthritis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Persistent synovial inflammation plays important roles in persistent pain development in the rat knee before cartilage degradation reaches the subchondral bone.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018 Aug 16;19(1):291. doi: 10.1186/s12891-018-2221-5. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018. PMID: 30115046 Free PMC article.
-
Grading of monosodium iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis reveals a concentration-dependent sensitization of nociceptors in the knee joint of the rat.Neurosci Lett. 2009 Nov 13;465(2):184-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2009.08.063. Epub 2009 Aug 27. Neurosci Lett. 2009. PMID: 19716399
-
Evaluation of monosodium iodoacetate dosage to induce knee osteoarthritis: Relation with oxidative stress and pain.Int J Rheum Dis. 2019 Mar;22(3):399-410. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.13450. Epub 2018 Dec 25. Int J Rheum Dis. 2019. PMID: 30585422
-
Joint unloading inhibits articular cartilage degeneration in knee joints of a monosodium iodoacetate-induced rat model of osteoarthritis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019 Jul;27(7):1084-1093. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2019.03.001. Epub 2019 Mar 16. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019. PMID: 30890456
-
Arthralgia.In: Walker HK, Hall WD, Hurst JW, editors. Clinical Methods: The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations. 3rd edition. Boston: Butterworths; 1990. Chapter 160. In: Walker HK, Hall WD, Hurst JW, editors. Clinical Methods: The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations. 3rd edition. Boston: Butterworths; 1990. Chapter 160. PMID: 21250146 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of exercise on the expression of nerve growth factor in the spinal cord of rats with induced osteoarthritis.J Phys Ther Sci. 2015 Aug;27(8):2551-4. doi: 10.1589/jpts.27.2551. Epub 2015 Aug 21. J Phys Ther Sci. 2015. PMID: 26357438 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of an oral preparation containing hyaluronic acid (Oralvisc®) on obese knee osteoarthritis patients determined by pain, function, bradykinin, leptin, inflammatory cytokines, and heavy water analyses.Rheumatol Int. 2015 Jan;35(1):43-52. doi: 10.1007/s00296-014-3047-6. Epub 2014 Jun 5. Rheumatol Int. 2015. PMID: 24899570 Clinical Trial.
-
Mitochondria in Injury, Inflammation and Disease of Articular Skeletal Joints.Front Immunol. 2021 Sep 3;12:695257. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.695257. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34539627 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

