Does joint alignment affect the T2 values of cartilage in patients with knee osteoarthritis?
- PMID: 20013272
- PMCID: PMC3696385
- DOI: 10.1007/s00330-009-1689-7
Does joint alignment affect the T2 values of cartilage in patients with knee osteoarthritis?
Abstract
Objective: To assess the relationship between T2 values of femorotibial cartilage and knee alignment in patients with clinical symptoms of medial osteoarthritis (OA).
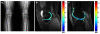
Methods: Twenty-four patients (mean age +/- standard deviation, 62.5 +/- 9.9 years) with clinical symptoms of medial knee OA, 12 with varus and 12 with valgus alignment of the femorotibial joint, were investigated on 3T MR using a 2D multi-echo spin echo (MESE) sequence for T2 mapping. Analysis of covariance, Spearman correlation coefficients, exact Mann-Whitney tests, and Fisher's exact tests were used for statistical analysis.
Results: Overall the T2 values of cartilage in the medial compartment (median +/- interquartile-range, 49.44 +/- 6.58) were significantly higher (P = 0.0043) than those in the lateral compartment (47.15 +/- 6.87). Patients with varus alignment (50.83 +/- 6.30 ms) had significantly higher T2 values of cartilage (P < 0.0001) than patients with valgus alignment (46.20 +/- 6.00 ms). No statistically significant association between the T2 values of cartilage (in either location) and the Kellgren Lawrence score was found in the varus or in the valgus group.
Conclusion: T2 measurements were increased in medial knee OA patients with varus alignment, adding support to the theory of an association of OA and joint alignment.
Figures

References
-
- Tetsworth K, Paley D. Malalignment and degenerative arthropathy. Orthop Clin North Am. 1994;25:367–377. - PubMed
-
- Schipplein OD, Andriacchi TP. Interaction between active and passive knee stabilizers during level walking. J Orthop Res. 1991;9:113–119. doi:10.1002/jor.1100090114. - PubMed
-
- Tanamas S, Hanna FS, Cicuttini FM, Wluka AE, Berry P, Urquhart DM. Does knee malalignment increase the risk of development and progression of knee osteoarthritis? A systematic review. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;61:459–467. doi:10.1002/art.24336. - PubMed
-
- Burstein D, Gray ML. Is MRI fulfilling its promise for molecular imaging of cartilage in arthritis? Osteoarthr Cartil. 2006;14:1087–1090. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2006.07.001. - PubMed
-
- Stahl R, Luke A, Li X, Carballido-Gamio J, Ma CB, Majumdar S, Link TM. T1rho, T2 and focal knee cartilage abnormalities in physically active and sedentary healthy subjects versus early OA patients–a 3.0-Tesla MRI study. Eur Radiol. 2009;19:132–143. doi:10.1007/s00330-008-1107-6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

