Image quality and diagnostic accuracy of unenhanced SSFP MR angiography compared with conventional contrast-enhanced MR angiography for the assessment of thoracic aortic diseases
- PMID: 20013276
- PMCID: PMC2861759
- DOI: 10.1007/s00330-009-1672-3
Image quality and diagnostic accuracy of unenhanced SSFP MR angiography compared with conventional contrast-enhanced MR angiography for the assessment of thoracic aortic diseases
Abstract
Objectives: The purpose of this study was to determine the image quality and diagnostic accuracy of three-dimensional (3D) unenhanced steady state free precession (SSFP) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) for the evaluation of thoracic aortic diseases.
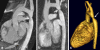
Methods: Fifty consecutive patients with known or suspected thoracic aortic disease underwent free-breathing ECG-gated unenhanced SSFP MRA with non-selective radiofrequency excitation and contrast-enhanced (CE) MRA of the thorax at 1.5 T. Two readers independently evaluated the two datasets for image quality in the aortic root, ascending aorta, aortic arch, descending aorta, and origins of supra-aortic arteries, and for abnormal findings. Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) were determined for both datasets. Sensitivity, specificity, and diagnostic accuracy of unenhanced SSFP MRA for the diagnosis of aortic abnormalities were determined.
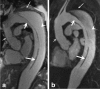
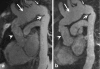
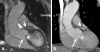
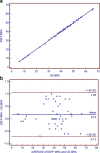
Results: Abnormal aortic findings, including aneurysm (n = 47), coarctation (n = 14), dissection (n = 12), aortic graft (n = 6), intramural hematoma (n = 11), mural thrombus in the aortic arch (n = 1), and penetrating aortic ulcer (n = 9), were confidently detected on both datasets. Sensitivity, specificity, and diagnostic accuracy of SSFP MRA for the detection of aortic disease were 100% with CE-MRA serving as a reference standard. Image quality of the aortic root was significantly higher on SSFP MRA (P < 0.001) with no significant difference for other aortic segments (P > 0.05). SNR and CNR values were higher for all segments on SSFP MRA (P < 0.01).
Conclusion: Our results suggest that free-breathing navigator-gated 3D SSFP MRA with non-selective radiofrequency excitation is a promising technique that provides high image quality and diagnostic accuracy for the assessment of thoracic aortic disease without the need for intravenous contrast material.
Figures
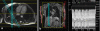
References
-
- Gebker R, Gomaa O, Schnackenburg B, Rebakowski J, Fleck E, Nagel E. Comparison of different MRI techniques for the assessment of thoracic aortic pathology: 3D contrast enhanced MR angiography, turbo spin-echo and balanced steady state free precession. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2007;23(6):747–756. doi: 10.1007/s10554-006-9204-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Prince MR, Narasimham DL, Jacoby WT, et al. Three-dimensional gadolinium-enhanced MR angiography of the thoracic aorta. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996;166:1387–1397. - PubMed
-
- Krinsky GA, Reuss PM, Lee VS, et al. Thoracic aorta: comparison of single-dose breath-hold and double-dose non-breath-hold gadolinium-enhanced three-dimensional MR angiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1999;173:145–150. - PubMed

