Reduced renal length and volume 20 years after very preterm birth
- PMID: 20013294
- PMCID: PMC2810374
- DOI: 10.1007/s00467-009-1371-y
Reduced renal length and volume 20 years after very preterm birth
Abstract
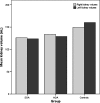
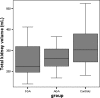
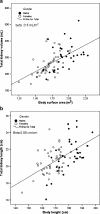
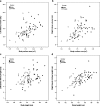
Intrauterine growth retardation is presumed to be associated with decreased renal size and impaired renal function as a result of stunted kidney development and nephron deficit. To study whether very preterm birth also affects renal size at young adulthood, we sonographically measured bipolar kidney length and volume in 51 very premature individuals (<32 weeks of gestation), either small (SGA) or appropriate (AGA) for gestational age (22 SGA and 29 AGA), and 30 full-term controls 20 years after birth. Relative kidney length and volume were calculated. Both absolute and relative left kidney length and volume were significantly lower in SGA and AGA individuals, notably in women. Renal size did not differ between SGA and AGA individuals. In 70% of controls, the left kidney was larger than the right one compared with 40.9% in SGA [relative risk (RR) 1.7; 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.0-3.0] and 48.3% in AGA (RR 1.5; 95% CI 0.9-2.3) individuals. Renal structural anomalies were present in eight prematurely born participants only. Our data suggest that kidney growth is stunted after preterm birth, especially on the left side, and in the female gender.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Renal function and size at young adult age after intrauterine growth restriction and very premature birth.Am J Kidney Dis. 2007 Oct;50(4):542-51. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2007.06.015. Am J Kidney Dis. 2007. PMID: 17900453
-
Very preterm birth is a risk factor for increased systolic blood pressure at a young adult age.Pediatr Nephrol. 2010 Mar;25(3):509-16. doi: 10.1007/s00467-009-1373-9. Epub 2009 Dec 15. Pediatr Nephrol. 2010. PMID: 20012998 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of gestational age and growth restriction on compensatory kidney growth.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009 Jan;24(1):142-8. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfn431. Epub 2008 Aug 4. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009. PMID: 18678558
-
Neurodevelopmental consequences of being born SGA.Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2005 Mar;2(3):372-7. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2005. PMID: 16429113 Review.
-
Ultrasound Measurement and Kidney Development: a Mini-Review for Nephrologists.Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2021 Jan-Feb;32(1):174-182. doi: 10.4103/1319-2442.318520. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2021. PMID: 34145128 Review.
Cited by
-
Adolescent Kidney Outcomes after Extremely Preterm Birth and Neonatal Acute Kidney Injury: There May be More to the Story.Am J Perinatol. 2024 May;41(S 01):e3319-e3325. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-1778038. Epub 2024 Jan 9. Am J Perinatol. 2024. PMID: 38195965 Free PMC article.
-
Kidney volume, kidney function, and ambulatory blood pressure in children born extremely preterm with and without nephrocalcinosis.Pediatr Nephrol. 2019 Oct;34(10):1765-1776. doi: 10.1007/s00467-019-04293-9. Epub 2019 Jul 23. Pediatr Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31338588 Free PMC article.
-
When the progresses in neonatology lead to severe congenital nephron deficit: is there a pilot in the NICU?Pediatr Nephrol. 2022 Jun;37(6):1277-1284. doi: 10.1007/s00467-021-05338-8. Epub 2021 Nov 10. Pediatr Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 34761299
-
Developmental origins of chronic renal disease: an integrative hypothesis.Int J Nephrol. 2013;2013:346067. doi: 10.1155/2013/346067. Epub 2013 Aug 29. Int J Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 24073334 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adrenal Steroid Metabolism and Blood Pressure in 5- to 7-Year-Old Children Born Preterm as Compared to Peers Born at Term.Front Pediatr. 2021 Nov 30;9:754989. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.754989. eCollection 2021. Front Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34917560 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

