Conservation of miR-15a/16-1 and miR-15b/16-2 clusters
- PMID: 20013340
- PMCID: PMC2820079
- DOI: 10.1007/s00335-009-9240-3
Conservation of miR-15a/16-1 and miR-15b/16-2 clusters
Abstract
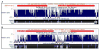
MiR-15a/16-1 and miR-15b/16-2 clusters have been shown to play very important roles in regulating cell proliferation and apoptosis by targeting cell cycle proteins and the antiapoptotic Bcl-2 gene. However, the physiological implications of those two clusters are largely elusive. By aligning the primary miR-15a/16-1 sequence among 44 vertebrates, we found that there was a gap in the homologous region of the rat genome. To verify that there was a similar miR-15a/16-1 cluster in rats, we amplified this region from rat genomic DNA using PCR and found that a 697-bp sequence was missing in the current rat genome database, which covers the miR-15a/16-1 cluster. Subsequently, we also investigated the expression pattern of individual miRNAs spliced from miR-15a/16-1 and miR-15b/16-2 clusters, including miR-15a, miR-15a*, miR-15b, miR-15b*, miR-16-1/2, and miR-16-1/2* from various rat tissues, and found that all of those miRNAs were expressed in the investigated tissues. MiR-16 was most expressed in the heart, followed by the brain, lung, kidney, and small intestine, which indicates tissue specificity for individual miRNA expression from both clusters. Our results demonstrated that both miR-15a/16-1 and miR-15b/16-2 clusters are highly conserved among mammalian species. The investigation of the biological functions of those two clusters using transgenic or knockout/knockdown models will provide new clues to understanding their implications in human diseases and finding a new approach for miRNA-based therapy.
Figures




References
-
- Aqeilan RI, Calin GA, Croce CM. miR-15a and miR-16-1 in cancer: discovery, function and future perspectives. Cell Death Differ. 2009 in press. - PubMed
-
- Bandi N, Zbinden S, Gugger M, Arnold M, Kocher V, et al. miR-15a and miR-16 are implicated in cell cycle regulation in a Rb-dependent manner and are frequently deleted or down-regulated in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2009;69:5553–5559. - PubMed
-
- Bilen J, Liu N, Burnett BG, Pittman RN, Bonini NM. MicroRNA pathways modulate polyglutamine-induced neurodegeneration. Mol Cell. 2006;24:157–163. - PubMed
-
- Bonci D, Coppola V, Musumeci M, Addario A, Giuffrida R, et al. The miR-15a-miR-16–1 cluster controls prostate cancer by targeting multiple oncogenic activities. Nat Med. 2008;14:1271–1277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

