California hospital leaders' views of hospitalists: meeting needs of the present and future
- PMID: 20013852
- PMCID: PMC5041305
- DOI: 10.1002/jhm.529
California hospital leaders' views of hospitalists: meeting needs of the present and future
Abstract
Background: Hospital medicine has grown rapidly, but hospital leaders' perceptions of current and future drivers of hospitalist growth are unknown.
Objective: : To determine hospital executives' perceptions of factors leading to hospitalist implementation and their vision for hospitalists' work roles.
Setting: Nonfederal, acute care hospitals in California.
Participants: California hospital leaders (eg, chief executive officers).
Intervention: Cross-sectional survey from 2006 to 2007.
Measurements: We asked California hospital leaders whether their hospitals had a hospitalist service and the prospects for growth. In addition, we examined factors responsible for implementation, scope of hospitalists' practices, and need for additional certification as perceived by hospital leaders.
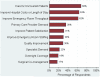
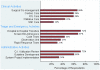
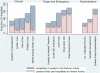
Results: We received surveys from 179 of 334 hospitals (response rate of 54%). Of the 64% of respondents that reported the use of hospitalists, none intended to decrease the size of their hospitalist group, and 57% expected growth over 2 years. The most common reasons for implementing a hospitalist program were to care for uncovered patients (68%) and improve cost/length of stay (63%). Respondents also indicated that demand from other physicians was an important factor. Leaders reported that hospitalists provide a wide range of services, with a majority involved in quality improvement projects (72%) and medical comanagement of surgical patients (66%). Most leaders favor additional certification for hospitalists.
Conclusions: There is widespread adoption of hospitalists in California hospitals, with an expectation of continued growth. The drivers of the field's growth are evolving and dynamic. In particular, attentiveness to quality performance and demand from other physicians are increasingly important reasons for implementation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Health care market trends and the evolution of hospitalist use and roles.J Gen Intern Med. 2005 Feb;20(2):101-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1497.2005.40184.x. J Gen Intern Med. 2005. PMID: 15836541 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the value of pediatric hospitalist programs: the perspective of hospital leaders.Acad Pediatr. 2009 May-Jun;9(3):192-6. doi: 10.1016/j.acap.2009.01.003. Epub 2009 Mar 9. Acad Pediatr. 2009. PMID: 19450780
-
Cross-sectional analysis of hospitalist prevalence and quality of care in California.J Hosp Med. 2010 Apr;5(4):200-7. doi: 10.1002/jhm.609. J Hosp Med. 2010. PMID: 20394024
-
Hospitalists as Facilitators of Surge and Contingency Medical Operations and Planning.Mil Med. 2024 Feb 27;189(3-4):70-73. doi: 10.1093/milmed/usad320. Mil Med. 2024. PMID: 37606620 Review.
-
Evolving practice of hospital medicine and its impact on hospital throughput and efficiencies.J Hosp Med. 2012 Oct;7(8):649-54. doi: 10.1002/jhm.1951. Epub 2012 Jul 12. J Hosp Med. 2012. PMID: 22791678 Review.
Cited by
-
The Hospital Medicine Reengineering Network (HOMERuN): a learning organization focused on improving hospital care.Acad Med. 2014 Mar;89(3):415-20. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000000139. Acad Med. 2014. PMID: 24448050 Free PMC article.
-
Triaging Inpatient Admissions: an Opportunity for Resident Education.J Gen Intern Med. 2019 May;34(5):754-757. doi: 10.1007/s11606-019-04882-2. J Gen Intern Med. 2019. PMID: 30993610 Free PMC article.
-
The association of hospital characteristics and quality improvement activities in inpatient medical services.J Gen Intern Med. 2014 May;29(5):715-22. doi: 10.1007/s11606-013-2759-8. Epub 2014 Jan 15. J Gen Intern Med. 2014. PMID: 24424776 Free PMC article.
-
Neurohospitalists: perceived need and training requirements in academic neurology.Neurohospitalist. 2014 Jan;4(1):9-17. doi: 10.1177/1941874413495880. Neurohospitalist. 2014. PMID: 24381705 Free PMC article.
-
Hospitalist utilization and hospital performance on 6 publicly reported patient outcomes.J Hosp Med. 2012 Jul-Aug;7(6):482-8. doi: 10.1002/jhm.1943. Epub 2012 Jun 11. J Hosp Med. 2012. PMID: 22689448 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Craig DE, Hartka L, Likosky WH, Caplan WM, Litsky P, Smithey J. Implementation of a hospitalist system in a large health maintenance organization: the Kaiser Permanente experience. Ann Intern Med. 1999;130:355–9. - PubMed
-
- Smith PC, Westfall JM, Nichols RA. Primary care family physicians and 2 hospitalist models: comparison of outcomes, processes, and costs. J Fam Pract. 2002;51:1021–7. - PubMed
-
- Molinari C, Short R. Effects of an HMO hospitalist program on inpatient utilization. Am J Manag Care. 2001;7:1051–7. - PubMed
-
- Wachter RM, Goldman L. The emerging role of "hospitalists" in the American health care system. N Engl J Med. 1996;335:514–7. - PubMed
-
- Sox HC. The hospitalist model: perspectives of the patient, the Internist, and internal medicine. Ann Intern Med. 1999;130:368–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

