PELP1: A novel therapeutic target for hormonal cancers
- PMID: 20014005
- PMCID: PMC2997573
- DOI: 10.1002/iub.287
PELP1: A novel therapeutic target for hormonal cancers
Abstract
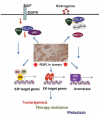
Recent studies implicate that the estrogen receptor (ER) coregulator proline-, glutamic acid-, and leucine-rich protein (PELP) 1 as playing critical roles in ER-genomic, ER-nongenomic, and ER-signaling cross talk with growth factor signaling pathways. PELP1 expression is deregulated in hormonal cancers and recent studies further elucidated the molecular mechanisms by which PELP1 regulates hormone therapy response. Although PELP1 is important for normal functions of the ER, the possibility to target ER-PELP1 axis appears to be an effective strategy for preventing hormonal carcinogenesis and therapy resistance. Thus, PELP1 may be useful as prognostic marker for hormonal cancers and PELP1 signaling may be useful to generate targeted therapeutics to overcome hormonal therapy resistance.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Emerging significance of ER-coregulator PELP1/MNAR in cancer.Histol Histopathol. 2007 Jan;22(1):91-6. doi: 10.14670/HH-22.91. Histol Histopathol. 2007. PMID: 17128415 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive analysis of recent biochemical and biologic findings regarding a newly discovered protein-PELP1/MNAR.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2006;23(1):1-7. doi: 10.1007/s10585-006-9019-9. Epub 2006 Jul 7. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2006. PMID: 16826428 Review.
-
Functional and biological properties of the nuclear receptor coregulator PELP1/MNAR.Nucl Recept Signal. 2007 May 17;5:e004. doi: 10.1621/nrs.05004. Nucl Recept Signal. 2007. PMID: 17525794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extranuclear coactivator signaling confers insensitivity to tamoxifen.Clin Cancer Res. 2009 Jun 15;15(12):4123-30. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2347. Epub 2009 May 26. Clin Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19470742 Free PMC article.
-
Extranuclear functions of ER impact invasive migration and metastasis by breast cancer cells.Cancer Res. 2010 May 15;70(10):4092-101. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3834. Epub 2010 May 11. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20460518 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Central role for PELP1 in nonandrogenic activation of the androgen receptor in prostate cancer.Mol Endocrinol. 2012 Apr;26(4):550-61. doi: 10.1210/me.2011-1101. Epub 2012 Mar 8. Mol Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22403175 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-cell adhesion regulates Merlin/NF2 interaction with the PAF complex.PLoS One. 2021 Aug 23;16(8):e0254697. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0254697. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34424918 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the PELP1-KDM1 axis as a potential therapeutic strategy for breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2012 Jul 19;14(4):R108. doi: 10.1186/bcr3229. Breast Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22812534 Free PMC article.
-
PELP1 overexpression in the mouse mammary gland results in the development of hyperplasia and carcinoma.Cancer Res. 2014 Dec 15;74(24):7395-405. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-0993. Epub 2014 Nov 6. Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25377474 Free PMC article.
-
Extranuclear signaling by estrogen: role in breast cancer progression and metastasis.Minerva Ginecol. 2010 Dec;62(6):573-83. Minerva Ginecol. 2010. PMID: 21079578 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Green KA, Carroll JS. Oestrogen-receptor-mediated transcription and the influence of co-factors and chromatin state. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2007;7:713–722. - PubMed
-
- Heldring N, Pike A, Andersson S, Matthews J, Cheng G, Hartman J, Tujague M, Strom A, Treuter E, Warner M, Gustafsson JA. Estrogen receptors: how do they signal and what are their targets. Physiol Rev. 2007;87:905–931. - PubMed
-
- Lewis-Wambi JS, Jordan VC. Treatment of Postmenopausal Breast Cancer with Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs) Breast Dis. 2005;24:93–105. - PubMed
-
- Song RX, Zhang Z, Santen RJ. Estrogen rapid action via protein complex formation involving ERalpha and Src. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2005;16:347–353. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

