Emerging roles of Kruppel-like factor 6 and Kruppel-like factor 6 splice variant 1 in ovarian cancer progression and treatment
- PMID: 20014424
- PMCID: PMC3060765
- DOI: 10.1002/msj.20150
Emerging roles of Kruppel-like factor 6 and Kruppel-like factor 6 splice variant 1 in ovarian cancer progression and treatment
Abstract
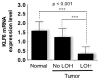
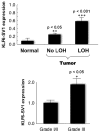
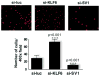
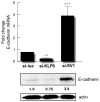
Epithelial ovarian cancer is one of the most lethal gynecologic cancers and the fifth most frequent cause of female cancer deaths in the United States. Despite dramatic treatment successes in other cancers through the use of molecular agents targeted against genetically defined events driving cancer development and progression, very few insights into epithelial ovarian cancer have been translated from the laboratory to the clinic. If advances are to be made in the early diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of this disease, it will be critical to characterize the common and private (personalized) genetic defects underlying the development and spread of epithelial ovarian cancer. The tumor suppressor Kruppel-like factor 6 and its alternatively spliced, oncogenic isoform, Kruppel-like factor 6 splice variant 1, are members of the Kruppel-like zinc finger transcription factor family of proteins, which have diverse roles in cellular differentiation, development, proliferation, growth-related signal transduction, and apoptosis. Inactivation of Kruppel-like factor 6 and overexpression of Kruppel-like factor 6 splice variant 1 have been associated with the progression of a number of human cancers and even with patient survival. This article summarizes our recent findings demonstrating that a majority of epithelial ovarian cancer tumors have Kruppel-like factor 6 allelic loss and decreased expression coupled with increased expression of Kruppel-like factor 6 splice variant 1. The targeted reduction of Kruppel-like factor 6 in ovarian cancer cell lines results in marked increases in cell proliferation, invasion, tumor growth, angiogenesis, and intraperitoneal dissemination in vivo. In contrast, the inhibition of Kruppel-like factor 6 splice variant 1 decreases cellular proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis, and tumorigenicity; this provides the rationale for its potential therapeutic application. These results and our recent demonstration that the inhibition of Kruppel-like factor 6 splice variant 1 can dramatically prolong survival in a preclinical mouse model of ovarian cancer are reviewed and discussed.
Copyright 2009 Mount Sinai School of Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURES
Figures


Similar articles
-
The role of KLF6 and its splice variants in cancer therapy.Drug Resist Updat. 2009 Feb-Apr;12(1-2):1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2008.11.001. Epub 2008 Dec 18. Drug Resist Updat. 2009. PMID: 19097929 Review.
-
Ras promotes growth by alternative splicing-mediated inactivation of the KLF6 tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma.Gastroenterology. 2008 May;134(5):1521-31. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.02.015. Epub 2008 Feb 13. Gastroenterology. 2008. PMID: 18471523 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of KLF6 and KLF6-SV1 in ovarian cancer progression and intraperitoneal dissemination.Clin Cancer Res. 2006 Jun 15;12(12):3730-9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0054. Clin Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16778100
-
KLF6-SV1 drives breast cancer metastasis and is associated with poor survival.Sci Transl Med. 2013 Jan 23;5(169):169ra12. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3004688. Sci Transl Med. 2013. PMID: 23345610 Free PMC article.
-
Biology of Krüppel-like factor 6 transcriptional regulator in cell life and death.IUBMB Life. 2010 Dec;62(12):896-905. doi: 10.1002/iub.396. IUBMB Life. 2010. PMID: 21154818 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-191 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation by has_circ_0000204/miR-191/KLF6 axis.Cell Prolif. 2019 Sep;52(5):e12635. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12635. Epub 2019 Jul 23. Cell Prolif. 2019. PMID: 31334580 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription Factors in Cancer: When Alternative Splicing Determines Opposite Cell Fates.Cells. 2020 Mar 20;9(3):760. doi: 10.3390/cells9030760. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32244895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lovastatin induced Kruppel like factor 2 (KLF2), Kruppel like factor 6 (KLF6) and Ras homolog family member B (RHOB) genes and preferentially led to viability reduction of Cisplatin-resistant cells.Oncotarget. 2017 Nov 16;8(63):106429-106442. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22472. eCollection 2017 Dec 5. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29290960 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of Krüppel-like factor 6 splice variant 1 in the development, diagnosis, and possible treatment strategies for non-small cell lung cancer.Am J Cancer Res. 2022 Oct 15;12(10):4468-4482. eCollection 2022. Am J Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36381325 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wnt activation promotes neuronal differentiation of glioblastoma.Cell Death Dis. 2013 Feb 21;4(2):e500. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.32. Cell Death Dis. 2013. PMID: 23429286 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;59:225–249. - PubMed
-
- Bieker JJ. Kruppel-like factors: three fingers in many pies. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:34355–34358. - PubMed
-
- Black AR, Black JD, Azizkhan-Clifford J. Sp1 and Kruppel-like factor family of transcription factors in cell growth regulation and cancer. J Cell Physiol. 2001;188:143–160. - PubMed
-
- Narla G, Heath KE, Reeves HL, et al. KLF6, a candidate tumor suppressor gene mutated in prostate cancer. Science. 2001;294:2563–2566. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

