Comparison of extensive protein fractionation and repetitive LC-MS/MS analyses on depth of analysis for complex proteomes
- PMID: 20014860
- PMCID: PMC2870931
- DOI: 10.1021/pr900927y
Comparison of extensive protein fractionation and repetitive LC-MS/MS analyses on depth of analysis for complex proteomes
Abstract
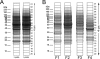
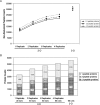
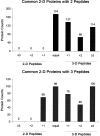
In-depth, reproducible coverage of complex proteomes is challenging because the complexity of tryptic digests subjected to LC-MS/MS analysis frequently exceeds mass spectrometer analytical capacity, which results in undersampling of data. In this study, we used cancer cell lysates to systematically compare the commonly used GeLC-MS/MS (1-D protein + 1-D peptide separation) method using four repetitive injections (2-D/repetitive) with a 3-D method that included solution isoelectric focusing and involved an equal number of LC-MS/MS runs. The 3-D method detected substantially more unique peptides and proteins, including higher numbers of unique peptides from low-abundance proteins, demonstrating that additional fractionation at the protein level is more effective than repetitive analyses at overcoming LC-MS/MS undersampling. Importantly, more than 90% of the 2-D/repetitive protein identifications were found in the 3-D method data in a direct protein level comparison, and the reproducibility between data sets increased to greater than 96% when factors such as database redundancy and use of rigid scoring thresholds were considered. Hence, high reproducibility of complex proteomes, such as human cancer cell lysates, readily can be achieved when using multidimensional separation methods with good depth of analysis.
Figures



References
-
- Cravatt B. F.; Simon G. M.; Yates J. R. III. The biological impact of mass-spectrometry-based proteomics. Nature 2007, 450 (7172), 991–1000. - PubMed
-
- Pasini E. M.; Kirkegaard M.; Salerno D.; Mortensen P.; Mann M.; Thomas A. W. Deep coverage mouse red blood cell proteome: a first comparison with the human red blood cell. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2008, 7 (7), 1317–30. - PubMed
-
- Dieguez-Acuna F. J.; Gerber S. A.; Kodama S.; Elias J. E.; Beausoleil S. A.; Faustman D.; Gygi S. P. Characterization of mouse spleen cells by subtractive proteomics. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2005, 4 (10), 1459–70. - PubMed
-
- Omenn G. S.; States D. J.; Adamski M.; Blackwell T. W.; Menon R.; Hermjakob H.; Apweiler R.; Haab B. B.; Simpson R. J.; Eddes J. S.; Kapp E. A.; Moritz R. L.; Chan D. W.; Rai A. J.; Admon A.; Aebersold R.; Eng J.; Hancock W. S.; Hefta S. A.; Meyer H.; Paik Y. K.; Yoo J. S.; Ping P.; Pounds J.; Adkins J.; Qian X.; Wang R.; Wasinger V.; Wu C. Y.; Zhao X.; Zeng R.; Archakov A.; Tsugita A.; Beer I.; Pandey A.; Pisano M.; Andrews P.; Tammen H.; Speicher D. W.; Hanash S. M. Overview of the HUPO Plasma Proteome Project: results from the pilot phase with 35 collaborating laboratories and multiple analytical groups, generating a core dataset of 3020 proteins and a publicly-available database. Proteomics 2005, 5 (13), 3226–45. - PubMed
-
- Chen E. I.; Hewel J.; Felding-Habermann B.; Yates J. R. III. Large scale protein profiling by combination of protein fractionation and multidimensional protein identification technology (MudPIT). Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2006, 5 (1), 53–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

