D-cycloserine and cocaine cue reactivity: preliminary findings
- PMID: 20014913
- PMCID: PMC2805418
- DOI: 10.3109/00952990903384332
D-cycloserine and cocaine cue reactivity: preliminary findings
Abstract
Background: D-cycloserine (DCS), a partial glutamate N-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA) receptor agonist, enhances extinction of conditioned fear responding in rodents and facilitates exposure-based learning in humans with anxiety disorders.
Objectives: This preliminary study investigates DCS pretreatment on response to cocaine cues in cocaine-dependent subjects.
Methods: Ten cocaine-dependent subjects were randomly assigned to receive either 50 mg DCS or matching placebo two hours before each of two 1-hour cocaine cue exposure sessions one day apart. HR and craving ratings were obtained before and during cue exposure sessions.
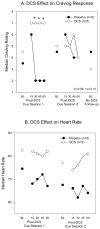
Results: There was a trend towards increased craving to cocaine cues in cocaine-dependent individuals after administration of DCS.
Conclusions: The administration of DCS prior to cue exposure sessions may facilitate response activation.
Scientific significance: While facilitation of extinction-based learning by DCS may have therapeutic potential for cocaine dependence, this drug may exhibit a different profile in cocaine-dependent individuals as compared to those with anxiety disorders.
Figures
Similar articles
-
D-cycloserine combined with cue exposure therapy fails to attenuate subjective and physiological craving in cocaine dependence.Am J Addict. 2015 Apr;24(3):217-224. doi: 10.1111/ajad.12191. Epub 2015 Mar 24. Am J Addict. 2015. PMID: 25808169 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A randomized, placebo-controlled laboratory study of the effects of D-cycloserine on craving in cocaine-dependent individuals.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013 Apr;226(4):739-46. doi: 10.1007/s00213-011-2592-x. Epub 2012 Jan 11. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013. PMID: 22234379 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
D-Cycloserine attenuates reactivity to smoking cues in nicotine dependent smokers: a pilot investigation.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2009 Oct 1;104(3):220-7. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2009.04.023. Epub 2009 Jul 9. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2009. PMID: 19592176 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
D-cycloserine effects on extinction of conditioned responses to drug-related cues.Biol Psychiatry. 2012 Jun 1;71(11):947-55. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.02.030. Biol Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 22579305 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of D-cycloserine on extinction: translation from preclinical to clinical work.Biol Psychiatry. 2006 Aug 15;60(4):369-75. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.03.084. Biol Psychiatry. 2006. PMID: 16919524 Review.
Cited by
-
The context dependency of extinction negates the effectiveness of cognitive enhancement to reduce cocaine-primed reinstatement.Behav Brain Res. 2013 Sep 1;252:444-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2013.06.026. Epub 2013 Jun 21. Behav Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23796972 Free PMC article.
-
Do specific NMDA receptor subunits act as gateways for addictive behaviors?Genes Brain Behav. 2017 Jan;16(1):118-138. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12348. Epub 2016 Nov 18. Genes Brain Behav. 2017. PMID: 27706932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
D-cycloserine combined with cue exposure therapy fails to attenuate subjective and physiological craving in cocaine dependence.Am J Addict. 2015 Apr;24(3):217-224. doi: 10.1111/ajad.12191. Epub 2015 Mar 24. Am J Addict. 2015. PMID: 25808169 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Epigenetics and biomarkers in the staging of neuropsychiatric disorders.Neurotox Res. 2010 Nov;18(3-4):347-66. doi: 10.1007/s12640-010-9163-5. Epub 2010 Mar 17. Neurotox Res. 2010. PMID: 20237880 Review.
-
Retrieval-Dependent Mechanisms Affecting Emotional Memory Persistence: Reconsolidation, Extinction, and the Space in Between.Front Behav Neurosci. 2020 Sep 29;14:574358. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2020.574358. eCollection 2020. Front Behav Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33132861 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Richardson R, Ledgerwood L, Cranney J. Facilitation of fear extinction by D-cycloserine: theoretical and clinical implications. Learn Mem. 2004;11(5):510–6. - PubMed
-
- Hofmann SG, et al. Augmentation of exposure therapy with D-cycloserine for social anxiety disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006;63(3):298–304. - PubMed
-
- Kushner MG, et al. D-cycloserine augmented exposure therapy for obsessive-compulsive disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 2007;62(8):835–8. - PubMed
-
- Ressler KJ, et al. Cognitive enhancers as adjuncts to psychotherapy: use of D-cycloserine in phobic individuals to facilitate extinction of fear. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2004;61(11):1136–44.1. - PubMed
-
- Botreau F, Paolone G, Stewart J. d-Cycloserine facilitates extinction of a cocaine-induced conditioned place preference. Behav Brain Res. 2006;172(1):173–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
