Aegyptin displays high-affinity for the von Willebrand factor binding site (RGQOGVMGF) in collagen and inhibits carotid thrombus formation in vivo
- PMID: 20015075
- PMCID: PMC2892622
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07494.x
Aegyptin displays high-affinity for the von Willebrand factor binding site (RGQOGVMGF) in collagen and inhibits carotid thrombus formation in vivo
Abstract
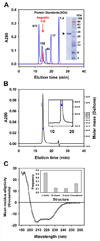
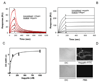
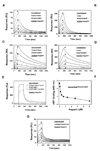
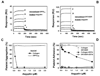
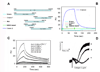
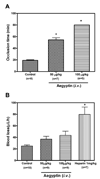
Aegyptin is a 30 kDa mosquito salivary gland protein that binds to collagen and inhibits platelet aggregation. We have studied the biophysical properties of aegyptin and its mechanism of action. Light-scattering plot showed that aegyptin has an elongated monomeric form, which explains the apparent molecular mass of 110 kDa estimated by gel-filtration chromatography. Surface plasmon resonance identified the sequence RGQOGVMGF (where O is hydroxyproline) that mediates collagen interaction with von Willebrand factor (vWF) as a high-affinity binding site for aegyptin, with a K(D) of approximately 5 nM. Additionally, aegyptin interacts with the linear peptide RGQPGVMGF and heat-denatured collagen, indicating that the triple helix and hydroxyproline are not a prerequisite for binding. However, aegyptin does not interact with scrambled RGQPGVMGF peptide. Aegyptin also recognizes the peptides (GPO)(10) and GFOGER with low affinity (microM range), which respectively represent glycoprotein VI and integrin alpha2beta1 binding sites in collagen. Truncated forms of aegyptin were engineered, and the C-terminus fragment was shown to interact with collagen and to attenuate platelet aggregation. In addition, aegyptin prevents laser-induced carotid thrombus formation in the presence of Rose Bengal in vivo, without significant bleeding in rats. In conclusion, aegyptin interacts with distinct binding sites in collagen, and is useful tool to inhibit platelet-collagen interaction in vitro and in vivo.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aegyptin, a novel mosquito salivary gland protein, specifically binds to collagen and prevents its interaction with platelet glycoprotein VI, integrin alpha2beta1, and von Willebrand factor.J Biol Chem. 2007 Sep 14;282(37):26928-26938. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M705669200. Epub 2007 Jul 24. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17650501 Free PMC article.
-
Simplagrin, a platelet aggregation inhibitor from Simulium nigrimanum salivary glands specifically binds to the Von Willebrand factor receptor in collagen and inhibits carotid thrombus formation in vivo.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014 Jun 12;8(6):e2947. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002947. eCollection 2014 Jun. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014. PMID: 24921659 Free PMC article.
-
Collagen-mimetic peptides mediate flow-dependent thrombus formation by high- or low-affinity binding of integrin alpha2beta1 and glycoprotein VI.J Thromb Haemost. 2008 Dec;6(12):2132-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2008.03167.x. Epub 2008 Sep 29. J Thromb Haemost. 2008. PMID: 18826391
-
Production and characterization of saratin, an inhibitor of von Willebrand factor-dependent platelet adhesion to collagen.Semin Thromb Hemost. 2001 Aug;27(4):337-48. doi: 10.1055/s-2001-16887. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2001. PMID: 11547356 Review.
-
von Willebrand factor fragments.Curr Stud Hematol Blood Transfus. 1991;(58):42-5. doi: 10.1159/000419335. Curr Stud Hematol Blood Transfus. 1991. PMID: 1954772 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The collαgen III fibril has a "flexi-rod" structure of flexible sequences interspersed with rigid bioactive domains including two with hemostatic roles.PLoS One. 2017 Jul 13;12(7):e0175582. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0175582. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28704418 Free PMC article.
-
Collagen binding specificity of the discoidin domain receptors: binding sites on collagens II and III and molecular determinants for collagen IV recognition by DDR1.Matrix Biol. 2011 Jan;30(1):16-26. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2010.10.004. Epub 2010 Oct 28. Matrix Biol. 2011. PMID: 21044884 Free PMC article.
-
Polyunsaturated fatty acids promote Plasmodium falciparum gametocytogenesis.Biol Open. 2019 Jul 16;8(7):bio042259. doi: 10.1242/bio.042259. Biol Open. 2019. PMID: 31221627 Free PMC article.
-
An insight into the sialome of blood-feeding Nematocera.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2010 Nov;40(11):767-84. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2010.08.002. Epub 2010 Aug 20. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20728537 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An insight into the sialotranscriptome and virome of Amazonian anophelines.BMC Genomics. 2019 Mar 4;20(1):166. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5545-0. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 30832587 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Khoshnoodi J, Cartailler JP, Alvares K, Veis A, Hudson BG. Molecular recognition in the assembly of collagens: terminal noncollagenous domains are key recognition modules in the formation of triple helical protomers. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:38117–38121. - PubMed
-
- Heino J. The collagen family members as cell adhesion proteins. Bioessays. 2007;29:1001–1010. - PubMed
-
- Nieswandt B, Watson SP. Platelet-collagen interaction: is GPVI the central receptor? Blood. 2003;102:449–461. - PubMed
-
- Savage B, Almus-Jacobs F, Ruggeri ZM. Specific synergy of multiple substrate-receptor interactions in platelet thrombus formation under flow. Cell. 1998;94:657–666. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

