An alpha-galactosylceramide C20:2 N-acyl variant enhances anti-inflammatory and regulatory T cell-independent responses that prevent type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 20015094
- PMCID: PMC2857941
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2009.04074.x
An alpha-galactosylceramide C20:2 N-acyl variant enhances anti-inflammatory and regulatory T cell-independent responses that prevent type 1 diabetes
Abstract
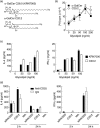
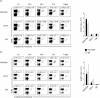
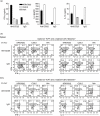
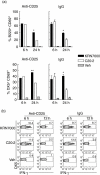
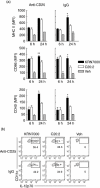
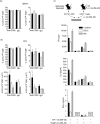
Protection from type 1 diabetes (T1D), a T helper type 1 (Th1)-mediated disease, is achievable in non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice by treatment with alpha-galactosylceramide (alpha-GalCer) glycolipids that stimulate CD1d-restricted invariant natural killer T (iNK T) cells. While we have reported previously that the C20:2 N-acyl variant of alpha-GalCer elicits a Th2-biased cytokine response and protects NOD mice from T1D more effectively than a form of alpha-GalCer that induces mixed Th1 and Th2 responses, it remained to determine whether this protection is accompanied by heightened anti-inflammatory responses. We show that treatment of NOD mice with C20:2 diminished the activation of 'inflammatory' interleukin (IL)-12 producing CD11c(high)CD8+ myeloid dendritic cells (mDCs) and augmented the function of 'tolerogenic' DCs more effectively than treatment with the prototypical iNKT cell activator KRN7000 (alpha-GalCer C26:0) that induces Th1- and Th2-type responses. These findings correlate with a reduced capacity of C20:2 to sustain the early transactivation of T, B and NK cells. They may also explain our observation that C20:2 activated iNK T cells depend less than KRN7000 activated iNK T cells upon regulation by regulatory T cells for cytokine secretion and protection from T1D. The enhanced anti-inflammatory properties of C20:2 relative to KRN7000 suggest that C20:2 should be evaluated further as a drug to induce iNK T cell-mediated protection from T1D in humans.
Figures

References
-
- Bendelac A, Savage PB, Teyton L. The biology of NKT cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007;25:297–336. - PubMed
-
- Kronenberg M. Toward an understanding of NKT cell biology: progress and paradoxes. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:877–900. - PubMed
-
- Van Kaer L. Alpha-galactosylceramide therapy for autoimmune diseases: prospects and obstacles. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:31–42. - PubMed
-
- Godfrey DI, MacDonald HR, Kronenberg M, Smyth MJ, Van Kaer L. NKT cells: what's in a name? Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:231–7. - PubMed
-
- Anderson MS, Bluestone JA. The NOD mouse: a model of immune dysregulation. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:447–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

