Cholesterol modulates ion channels via down-regulation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate
- PMID: 20015154
- PMCID: PMC2891522
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06545.x
Cholesterol modulates ion channels via down-regulation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate
Abstract
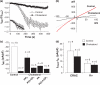
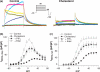
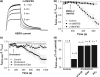
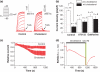
Ubiquitously expressed Mg(2+)-inhibitory cation (MIC) channels are permeable to Ca2+ and Mg2+ and are essential for cell viability. When membrane cholesterol level was increased by pre-incubating cells with a water-soluble form of cholesterol, the endogenous MIC current in HEK293 cells was negatively regulated. The application of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) recovered MIC current from cholesterol effect. As PIP2 is the direct modulator for MIC channels, high cholesterol content may cause down-regulation of PIP2. To test this possibility, we examined the effect of cholesterol on two exogenously expressed PIP2-sensitive K+ channels: human Ether-a-go-go related gene (HERG) and KCNQ. Enrichment with cholesterol inhibited HERG currents, while inclusion of PIP2 in the pipette solution blocked the cholesterol effect. KCNQ channel was also inhibited by cholesterol. The effects of cholesterol on these channels were blocked by pre-incubating cells with inhibitors for phospholipase C, which may indicate that cholesterol enrichment induces the depletion of PIP2 via phospholipase C activation. Lipid analysis showed that cholesterol enrichment reduced gamma-(32)P incorporation into PIP2 by approximately 35%. Our results suggest that cholesterol may modulate ion channels by changing the levels of PIP2. Thus, an important cross-talk exists among two plasma membrane-enriched lipids, cholesterol and PIP2.
Figures
References
-
- Aarts M, Iihara K, Wei WL, Xiong ZG, Arundine M, Cerwinski W, MacDonald JF, Tymianski M. A key role for TRPM7 channels in anoxic neuronal death. Cell. 2003;115:863–877. - PubMed
-
- Bae YS, Lee TG, Park JC, Hur JH, Kim Y, Heo K, Kwak JY, Suh PG, Ryu SH. Identification of a compound that directly stimulates phospholipase C activity. Mol. Pharmacol. 2003;63:1043–1050. - PubMed
-
- Bian J, Cui J, McDonald TV. HERG K+ channel activity is regulated by changes in phosphatidyl inositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Circ. Res. 2001;89:1168–1176. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

