A novel pathway for receptor-mediated post-translational activation of inducible nitric oxide synthase
- PMID: 20015194
- PMCID: PMC2888614
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00992.x
A novel pathway for receptor-mediated post-translational activation of inducible nitric oxide synthase
Abstract
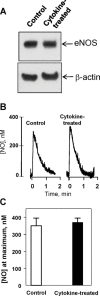
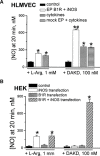
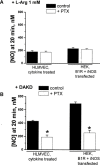
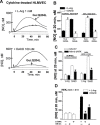
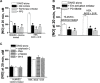
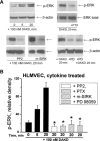
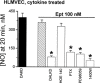
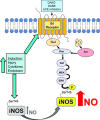
Inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) is a major source of nitric oxide during inflammation whose activity is thought to be controlled primarily at the expression level. The B1 kinin receptor (B1R) post-translationally activates iNOS beyond its basal activity via extracellular signal regulated kinase (ERK)-mediated phosphorylation of Ser(745) . Here we identified the signalling pathway causing iNOS activation in cytokine-treated endothelial cells or HEK293 cells transfected with iNOS and B1R. To allow kinetic measurements of nitric oxide release, we used a sensitive porphyrinic microsensor (response time = 10 msec.; 1 nM detection limit). B1Rs signalled through Gαi coupling as ERK and iNOS activation were inhibited by pertussis toxin. Furthermore, transfection of constitutively active mutant Gαi Q204L but not Gαq Q209L resulted in high basal iNOS-derived nitric oxide. G-βγ subunits were also necessary as transfection with the β-adrenergic receptor kinase C-terminus inhibited the response. B1R-dependent iNOS activation was also inhibited by Src family kinase inhibitor PP2 and trans-fection with dominant negative Src. Other ERK-MAP kinase members were involved as the response was inhibited by dominant negative H-Ras, Raf kinase inhibitor, ERK activation inhibitor and MEK inhibitor PD98059. In contrast, PI3 kinase inhibitor LY94002, calcium chelator 1,2-bis-(o-Aminophenoxy)-ethane-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid, tetraacetoxymethyl ester (BAPTA-AM), protein kinase C inhibitor calphostin C and protein kinase C activator PMA had no effect. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor enalaprilat also directly activated B1Rs to generate high output nitric oxide via the same pathway. These studies reveal a new mechanism for generating receptor-regulated high output nitric oxide in inflamed endothelium that may play an important role in the development of vascular inflammation.
© 2011 The Authors Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine © 2011 Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine/Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Beta-arrestin 2 is required for B1 receptor-dependent post-translational activation of inducible nitric oxide synthase.FASEB J. 2010 Jul;24(7):2475-83. doi: 10.1096/fj.09-148783. Epub 2010 Mar 12. FASEB J. 2010. PMID: 20228252 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic receptor-dependent activation of inducible nitric-oxide synthase by ERK-mediated phosphorylation of Ser745.J Biol Chem. 2007 Nov 2;282(44):32453-61. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M706242200. Epub 2007 Sep 5. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17804409
-
Endothelial nitric-oxide synthase activation generates an inducible nitric-oxide synthase-like output of nitric oxide in inflamed endothelium.J Biol Chem. 2013 Feb 8;288(6):4174-93. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.436022. Epub 2012 Dec 19. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23255592 Free PMC article.
-
Differential regulation of inducible and endothelial nitric oxide synthase by kinin B1 and B2 receptors.Neuropeptides. 2010 Apr;44(2):145-54. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2009.12.004. Epub 2010 Jan 4. Neuropeptides. 2010. PMID: 20045558 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kinin- and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor-mediated nitric oxide production in endothelial cells.Biol Chem. 2006 Feb;387(2):159-65. doi: 10.1515/BC.2006.021. Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16497147 Review.
Cited by
-
Diabetic Microvascular Disease: An Endocrine Society Scientific Statement.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017 Dec 1;102(12):4343-4410. doi: 10.1210/jc.2017-01922. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017. PMID: 29126250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amelioration of cardiac function and activation of anti-inflammatory vasoactive peptides expression in the rat myocardium by low level laser therapy.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 3;9(7):e101270. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101270. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24991808 Free PMC article.
-
Kininase 1 As a Preclinical Therapeutic Target for Kinin B1 Receptor in Insulin Resistance.Front Pharmacol. 2017 Aug 2;8:509. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00509. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28824433 Free PMC article.
-
The complex alteration in the network of IL-17-type cytokines in patients with hereditary angioedema.Clin Exp Med. 2018 Aug;18(3):355-361. doi: 10.1007/s10238-018-0499-0. Epub 2018 Apr 6. Clin Exp Med. 2018. PMID: 29623491
-
A primary role for kinin B1 receptor in inflammation, organ damage, and lethal thrombosis in a rat model of septic shock in diabetes.Eur J Inflamm. 2015 Apr 1;13(1):40-52. doi: 10.1177/1721727X15577736. Eur J Inflamm. 2015. PMID: 26413099 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Papapetropoulos A, Rudic RD, Sessa WC. Molecular control of nitric oxide synthases in the cardiovascular system. Cardiovasc Res. 1999;43:509–20. - PubMed
-
- Dudzinski DM, Igarashi J, Greif D, et al. The regulation and pharmacology of endothelial nitric oxide synthases. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2006;46:235–76. - PubMed
-
- Maniatis NA, Brovkovych V, Allen SE, et al. Novel mechanism of endothelial nitric oxide synthase activation mediated by caveolae internalization in endothelial cells. Circ Res. 2006;99:870–7. - PubMed
-
- Kone BC, Kuncewicz T, Zhang W, et al. Protein interactions with nitric oxide synthases: controlling the right time, the right place, and the right amount of nitric oxide. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003;285:F178–90. - PubMed
-
- Kleinert H, Schwarz PM, Forstermann U. Regulation of the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase. Biol Chem. 2003;384:1343–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

