Clinical outcomes in non-small-cell lung cancer patients with EGFR mutations: pooled analysis
- PMID: 20015198
- PMCID: PMC3837609
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00991.x
Clinical outcomes in non-small-cell lung cancer patients with EGFR mutations: pooled analysis
Abstract
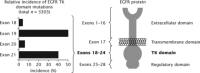
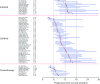
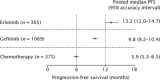
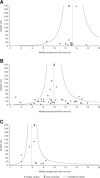
Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is a distinct subgroup of NSCLCs that is particularly responsive to EGFR tyrosine-kinase inhibitors (TKIs). A weighted pooled analysis of available studies was performed to evaluate clinical outcome in patients with EGFR-mutated NSCLC who were treated with chemotherapy or EGFR TKIs. Median progression-free survival (PFS) times were pooled from prospective or retrospective studies that evaluated chemotherapy or single-agent EGFR TKIs (erlotinib or gefitinib) in patients with NSCLC and EGFR mutations. Among the studies identified for inclusion in the analysis, 12 evaluated erlotinib (365 patients), 39 evaluated gefitinib (1069 patients) and 9 evaluated chemotherapy (375 patients). Across all studies, the most common EGFR mutations were deletions in exon 19 and the L858R substitution in exon 21. In the weighted pooled analysis, the overall median PFS was 13.2 months with erlotinib, 9.8 months with gefitinib and 5.9 months with chemotherapy. Using a two-sided permutation, erlotinib and gefitinib produced a longer median PFS versus chemotherapy, both individually (P= 0.000 and P= 0.002, respectively) and as a combined group (EGFR TKI versus chemotherapy, P= 0.000). EGFR TKIs appear to be the most effective treatment for patients with advanced EGFR-mutant NSCLC. Ongoing prospective trials comparing the efficacy of first-line chemotherapy and EGFR TKIs in EGFR-mutant disease should provide further insight into the most appropriate way to treat this specific group of patients.
Figures

Comment in
-
Response to 'Clinical outcomes in NSCLC patients with EGFR mutations: pooled analysis' (Paz-Ares et al., J Cell Mol Med. 2010; 14: 51-69).J Cell Mol Med. 2010 Nov;14(11):2693-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01188.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2010. PMID: 21029366 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2129–39. - PubMed
-
- Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004;304:1497–500. - PubMed
-
- Shepherd FA, Rodrigues Pereira J, Ciuleanu T, et al. Erlotinib in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:123–32. - PubMed
-
- Bezjak A, Tu D, Seymour L, et al. Symptom improvement in lung cancer patients treated with erlotinib: quality of life analysis of the National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group Study BR.21. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:3831–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

