Small leucine-rich proteoglycans in atherosclerotic lesions: novel targets of chronic statin treatment?
- PMID: 20015203
- PMCID: PMC3822791
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00986.x
Small leucine-rich proteoglycans in atherosclerotic lesions: novel targets of chronic statin treatment?
Abstract
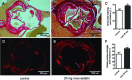
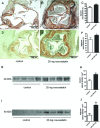
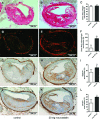
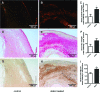
Small leucine-rich proteoglycans (SLRPs), such as decorin and biglycan, regulate the assembly and turnover of collagenous matrix. The aim of the study was to analyse the effect of chronic rosuvastatin treatment on decorin, biglycan and the collagen matrix in ApoE-deficient mice. Twenty-week-old male ApoE-deficient mice received normal chow or 20 mg rosuvastatin/kg × day for 32 weeks. Subsequently, matrix composition was analysed by histochemistry and immunostaining at the aortic root and in innominate arteries of ApoE deficient mice as well as in human carotid endarterectomy specimens. Immunoblotting of proteoglycans was performed from aortic extracts of ApoE-deficient mice. Immunohistochemistry and immunoblotting revealed strongly increased decorin and biglycan deposition in atherosclerotic plaques at the aortic root and in innominate arteries. In contrast, versican and perlecan expression was not changed by rosuvastatin. Furthermore, matrix metalloproteinase 2 and gelatinolytic activity were decreased in response to rosuvastatin and a condensed collagen-rich matrix was formed. In carotid endarterectomy specimens of statin-treated patients increased decorin and biglycan accumulation was detected as well. Drug treatment did not change low-density lipoprotein (LDL) plasma levels in ApoE-deficient mice and did not significantly affect lipid retention at the aortic root level as demonstrated by oil-red O staining and immunohistochemistry of LDL. Long-term treatment with rosuvastatin caused pronounced remodelling of atherosclerotic plaque matrix characterized specifically by enrichment with SLRPs and formation of a condensed collagen matrix. Therefore, decorin and biglycan might represent novel targets of statin treatment that contribute to a stable plaque phenotype.
© 2011 The Authors Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine © 2011 Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine/Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Rosuvastatin exerts favourable effects on thrombosis and neointimal growth in a mouse model of endothelial injury.Thromb Haemost. 2005 Jan;93(1):145-52. doi: 10.1160/TH04-07-0415. Thromb Haemost. 2005. PMID: 15630505
-
Proteoglycans and diseases of soft tissues.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;802:49-58. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-7893-1_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014. PMID: 24443020 Review.
-
Long-term treatment with the AT1-receptor antagonist telmisartan inhibits biglycan accumulation in murine atherosclerosis.Basic Res Cardiol. 2010 Jan;105(1):29-38. doi: 10.1007/s00395-009-0051-1. Epub 2009 Aug 23. Basic Res Cardiol. 2010. PMID: 19701787
-
[Impact of rosuvastatin on atherosclerosis lesions in apolipoprotein E knockout mice].Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2011 Aug;39(8):743-8. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 22169423 Chinese.
-
Differential roles for small leucine-rich proteoglycans in bone formation.Eur Cell Mater. 2003 Oct 6;6:12-21; discussion 21. doi: 10.22203/ecm.v006a02. Eur Cell Mater. 2003. PMID: 14562268 Review.
Cited by
-
Deficiency of biglycan causes cardiac fibroblasts to differentiate into a myofibroblast phenotype.J Biol Chem. 2011 May 13;286(19):17365-75. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.192682. Epub 2011 Mar 18. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21454527 Free PMC article.
-
Statins as anti-inflammatory agents in atherogenesis: molecular mechanisms and lessons from the recent clinical trials.Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18(11):1519-30. doi: 10.2174/138161212799504803. Curr Pharm Des. 2012. PMID: 22364136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteoglycan-driven Autophagy: A Nutrient-independent Mechanism to Control Intracellular Catabolism.J Histochem Cytochem. 2020 Nov;68(11):733-746. doi: 10.1369/0022155420937370. Epub 2020 Jul 6. J Histochem Cytochem. 2020. PMID: 32623955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Possible dual role of decorin in abdominal aortic aneurysm.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 17;10(3):e0120689. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120689. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25781946 Free PMC article.
-
A role for proteoglycans in vascular disease.Matrix Biol. 2018 Oct;71-72:396-420. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2018.02.019. Epub 2018 Feb 27. Matrix Biol. 2018. PMID: 29499356 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Randomised trial of cholesterol lowering in 4444 patients with coronary heart disease: the Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study (4S) Lancet. 1994;344:1383–9. - PubMed
-
- Heart Protection Study Collaborative Group. MRC/BHF Heart Protection Study of cholesterol lowering with simvastatin in 20,536 high-risk individuals: a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2002;360:7–22. - PubMed
-
- Maron DJ, Fazio S, Linton MF. Current perspectives on statins. Circulation. 2000;101:207–13. - PubMed
-
- Ridker PM, Rifai N, Pfeffer MA, et al. Long-term effects of pravastatin on plasma concentration of C-reactive protein. The Cholesterol and Recurrent Events (CARE) Investigators. Circulation. 1999;100:230–5. - PubMed
-
- Sparrow CP, Burton CA, Hernandez M, et al. Simvastatin has anti-inflammatory and antiatherosclerotic activities independent of plasma cholesterol lowering. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2001;21:115–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

