Testis response to low doses of cadmium in Wistar rats
- PMID: 20015210
- PMCID: PMC2965898
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2613.2009.00692.x
Testis response to low doses of cadmium in Wistar rats
Abstract
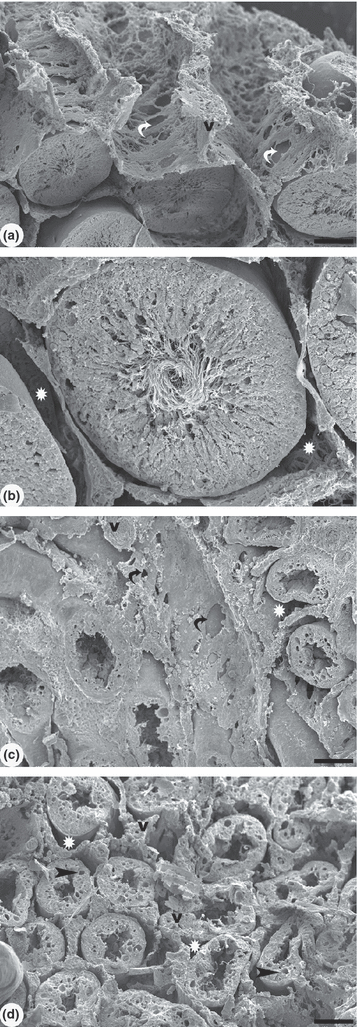
Although it is well known that cadmium (Cd) causes adverse effects on male rat reproductive organs, few studies have quantified alterations caused by its low doses. Quantification of these alterations, especially in the testis, was measured using morphometry. A single dose of cadmium chloride (1 or 1.2 mg/kg BW) was injected i.p. in adult rats, killed after 7 or 56 days. The lower dose caused slight alterations as measured by morphometrical analysis. The higher dose caused significant reduction in testis and epididymis weight, gonadossomatic index and length of seminiferous tubule (ST) after 7 and 56 days. Cadmium significantly reduced the ST diameter after 56 days. Decreased volume density of ST, after 7 and 56 days, was accompanied by an increase in interstitium volume density. The damage caused by the dose of 1.2 mg/kg can be clearly observed with light microscope. After 7 days, the tubule lumens were filled with degenerated germ cells and multinucleated spermatid aggregates. Vacuolization of the seminiferous epithelium was also observed. After 56 days, increased damage resulted in vacuolated ST, consisting only of Sertoli cells. Scanning electron microscopy examination of the testis showed that, in the group cadmium treated (1.2 mg/kg) and killed after 56 days, the interstitial tissue presents a compact and fibrous appearance with absence of fenestrae. The seminiferous epithelium height diminished and the absence of spermatozoa can be noted. The results show that a very small difference of Cd dose causes a sudden increase in testicular damage, apparently overpowering this tissue's natural defences.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of Arctium lappa on Cadmium-Induced Damage to the Testis and Epididymis of Adult Wistar Rats.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2016 Oct;173(2):362-71. doi: 10.1007/s12011-016-0663-x. Epub 2016 Mar 1. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2016. PMID: 26926909
-
Effect of orally administered cadmium on in situ pH, PCO2, and bicarbonate concentration in rat testis and epididymis.J Toxicol Environ Health. 1994 Jul;42(3):323-30. doi: 10.1080/15287399409531882. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1994. PMID: 8021965
-
Morphometric studies of development of the rat testis under physiological conditions and after CdCl2 poisoning.Acta Morphol Hung. 1986;34(1-2):53-7. Acta Morphol Hung. 1986. PMID: 3105261
-
Toxic effects of cadmium on testis of birds and mammals: a review.Anim Reprod Sci. 2015 Apr;155:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.anireprosci.2015.01.007. Epub 2015 Jan 31. Anim Reprod Sci. 2015. PMID: 25726439 Review.
-
Revisiting cadmium-induced toxicity in the male reproductive system: an update.Arch Toxicol. 2024 Nov;98(11):3619-3639. doi: 10.1007/s00204-024-03871-7. Epub 2024 Sep 24. Arch Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39317800 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Effects of Ethanolic Extract of Polygonum limbatum meism Against Reproductive Toxicity Induced by Cadmium in Male Guinea Pigs (Cavia porcellus).Front Vet Sci. 2021 Oct 12;8:736836. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.736836. eCollection 2021. Front Vet Sci. 2021. PMID: 34712722 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of pre-fixation delay and freezing on mink testicular endpoints for environmental research.PLoS One. 2015 May 1;10(5):e0125139. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125139. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25933113 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin modulates Nrf2 activity to protect porcine pre-pubertal Sertoli cells from the abnormal H2 O2 generation and reductive stress effects of cadmium.J Pineal Res. 2022 Aug;73(1):e12806. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12806. Epub 2022 May 24. J Pineal Res. 2022. PMID: 35524288 Free PMC article.
-
Sexually selected size differences and conserved sexual monomorphism of genital cortex.J Comp Neurol. 2017 Aug 15;525(12):2706-2718. doi: 10.1002/cne.24237. Epub 2017 May 30. J Comp Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28472863 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of grape seed extract against cadmium-induced testicular dysfunction.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Apr;13(4):3101-9. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.4928. Epub 2016 Feb 23. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 26935153 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Biswas NM, Gupta RS, Chattopadhyay A, Choudhury GR, Sarkar M. Effect of atenolol on cadmium-induced testicular toxicity in male rats. Reprod. Toxicol. 2001;15:699–704. - PubMed
-
- Blanco A, Moyano R, Vivo J, et al. Quantitative changes in the testicular structure in mice exposed to low doses of cadmium. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007;23:96–101. - PubMed
-
- Burukoğlu D, Bayçu C. Protective effects of zinc on testes of cadmium-treated rats. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008;81:521–524. - PubMed
-
- Clark RV. Three-dimensional organization of testicular interstitial tissue and lymphatic space in the rat. Anat. Rec. 1976;184:203–225. - PubMed
-
- Creasy DM. Pathogenesis of male reproductive toxicity. Toxicol. Pathol. 2001;29:64–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

