Modulatory effects of neuropsychopharmaca on intracellular pH of hippocampal neurones in vitro
- PMID: 20015293
- PMCID: PMC2825368
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00540.x
Modulatory effects of neuropsychopharmaca on intracellular pH of hippocampal neurones in vitro
Abstract
Background and purpose: The intracellular pH (pHi) of neurones is tightly regulated by, for example, membrane-bound acid-exchangers and loaders. Nevertheless, excessive bioelectric activity lowers steady-state pHi. In turn, even a moderate acidification can inhibit neuronal activity, a process believed to be part of a negative feedback loop controlling neuronal excitation. As moclobemide, an antidepressant, and also some antiepileptic drugs can reduce neuronal pHi in hippocampus slices in vitro, we screened a panel of currently used neuropsychopharmaca for comparable effects.
Experimental approach: BCECF-AM loaded hippocampal slices were superfused with 16 different neuroleptics, antidepressants and antiepileptics under bicarbonate-buffered conditions. Changes in steady-state pHi of CA3 neurones were measured fluorometrically.
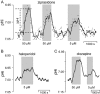
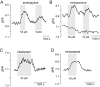
Key results: The antipsychotics haloperidol, clozapine, ziprasidone, and the antidepressants amitriptyline, doxepin, trimipramine, citalopram, mirtazapine, as well as the anticonvulsive drug tiagabine reversibly reduced the steady-state pHi by up to 0.35 pH-units in concentrations of 5-50 microM. In contrast, venlafaxine, the anticonvulsants carbamazepine, clonazepam, gabapentin, lamotrigine, zonisamide, and the mood stabilizer lithium had no effect on neuronal pHi.
Conclusion and implications: These data substantiate the view that clinically relevant concentrations of neuroleptics and antidepressants can mediate changes in neuronal pHi, which may contribute to their pharmacological mode of action. Effects on pHi should be taken into account when therapeutic or even harmful effects of these drugs are evaluated.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Neuropsychopharmaca influence the intracellular pH value of central neurons].Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr. 2012 Apr;80(4):201-12. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1273231. Epub 2011 May 19. Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr. 2012. PMID: 21598206 German.
-
Antiepileptic activity of zonisamide on hippocampal CA3 neurons does not depend on carbonic anhydrase inhibition.Epilepsy Res. 2008 May;79(2-3):105-11. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2007.11.009. Epub 2008 Mar 21. Epilepsy Res. 2008. PMID: 18359199
-
Levetiracetam inhibits Na+-dependent Cl-/HCO3- exchange of adult hippocampal CA3 neurons from guinea-pigs.Br J Pharmacol. 2004 Aug;142(7):1073-80. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705836. Epub 2004 Jul 12. Br J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15249428 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between antiepileptic and antipsychotic drugs.Drug Saf. 2006;29(2):95-118. doi: 10.2165/00002018-200629020-00001. Drug Saf. 2006. PMID: 16454538 Review.
-
Treatments for late-life bipolar disorder.Am J Geriatr Pharmacother. 2006 Dec;4(4):347-64. doi: 10.1016/j.amjopharm.2006.12.007. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother. 2006. PMID: 17296540 Review.
Cited by
-
Potential for New Therapeutic Approaches by Targeting Lactate and pH Mediated Epigenetic Dysregulation in Major Mental Diseases.Biomedicines. 2024 Feb 18;12(2):457. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12020457. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38398057 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Quantum Dot-Based pH Probe for Long-Term Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy Experiments in Living Cells.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022 Jan 19;14(2):2578-2586. doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c19926. Epub 2022 Jan 10. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022. PMID: 35001616 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 Outcomes: Does the Use of Psychotropic Drugs Make a Difference? Accumulating Evidence of a Beneficial Effect of Antidepressants-A Scoping Review.J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2022 May-Jun 01;42(3):284-292. doi: 10.1097/JCP.0000000000001543. Epub 2022 Apr 14. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35420565 Free PMC article.
-
Aging is associated with a mild acidification in neocortical human neurons in vitro.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2018 Oct;125(10):1495-1501. doi: 10.1007/s00702-018-1904-2. Epub 2018 Jul 11. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2018. PMID: 29995171
-
Effects of pH alterations on stress- and aging-induced protein phase separation.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Jun 24;79(7):380. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04393-0. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35750966 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amato A, Ballerini C, Attwell D. Intracellular pH changes produced by glutamate uptake in rat hippocampal slices. J Neurophysiol. 1994;72:1686–1696. - PubMed
-
- Benavides J, Martin A, Ugarte M, Valdivieso F. Inhibition by valproic acid of pyruvate uptake by brain mitochondria. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982;31:1633–1636. - PubMed
-
- Bevensee MO, Schwiening CF, Boron WF. Use of BCECF and propidium iodide to assess membrane integrity of acutely isolated CA1 neurones from rat hippocampus. J Neurosci Methods. 1995;58:61–75. - PubMed
-
- Bitran JA, Potter WZ, Manji HK, Gusovsky F. Chronic Li+ attenuates agonist- and phorbol ester-mediated Na+/H+ antiporter activity in HL 60 cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990;188:193–202. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

