C/EBPβ expression in ALK-positive anaplastic large cell lymphomas is required for cell proliferation and is induced by the STAT3 signaling pathway
- PMID: 20015877
- PMCID: PMC2864382
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2009.014050
C/EBPβ expression in ALK-positive anaplastic large cell lymphomas is required for cell proliferation and is induced by the STAT3 signaling pathway
Abstract
Background: Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma is characterized by the t(2;5) chromosomal translocation, resulting in the expression of a fusion protein formed of nucleophosmin (NPM) and ALK. Recently, we reported the abnormal expression of the transcription factor CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-beta (C/EBPbeta) in ALK-positive anaplastic large cell lymphomas, and demonstrated its dependence on NPM-ALK activity.
Design and methods: In this study, the role of C/EBPbeta in proliferation and survival of ALK-positive anaplastic large cell lymphomas was investigated, as well as the mechanism of its expression and activity. Highly effective short hairpin RNA sequences and/or pharmacological inhibitors were used to abrogate the expression or activity of C/EBPbeta, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), AKT, extracellular signal-related kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR).
Results: Interference with C/EBPbeta expression resulted in a dramatic decrease in cell proliferation in ALK-positive anaplastic large cell lymphomas, with a mild induction of apoptosis after 6 days. Down-regulation of STAT3 resulted in a marked decrease in C/EBPbeta mRNA and protein levels with impairment in cell proliferation and viability, underscoring the important role of these two proteins in ALK-mediated oncogenesis. Additionally, we demonstrated that reduction of ERK1/2 activity led to C/EBPbeta Thr(235) dephosphorylation and moderate growth retardation. The AKT/mTOR signaling pathway did not have any influence on C/EBPbeta expression or C/EBPbeta phosphorylation.
Conclusions: These findings reveal the convergence of STAT3 and ERK1/2 signaling pathways activated by NPM-ALK in mediating the regulation of C/EBPbeta expression, a transcription factor central to NPM-ALK transformation.
Figures
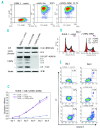

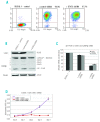

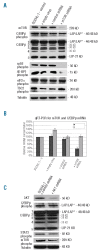
References
-
- Iwahara T, Fujimoto J, Wen D, Cupples R, Bucay N, Arakawa T, et al. Molecular characterization of ALK, a receptor tyrosine kinase expressed specifically in the nervous system. Oncogene. 1997;14(4):439–49. - PubMed
-
- Duyster J, Bai RY, Morris SW. Translocations involving anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) Oncogene. 2001;20(10):5623–37. - PubMed
-
- Chiarle R, Voena C, Ambrogio C, Piva R, Inghirami G. The anaplastic lymphoma kinase in the pathogenesis of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8(1):11–23. - PubMed
-
- Bai RY, Ouyang T, Miething C, Morris SW, Peschel C, Duyster J. Nucliophosmin-anaplastic lymphoma kinase associated with anaplastic large-cell lymphoma activates the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt antiapoptotic signaling pathway. Blood. 2000;96(13):4319–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

