ICP27 phosphorylation site mutants display altered functional interactions with cellular export factors Aly/REF and TAP/NXF1 but are able to bind herpes simplex virus 1 RNA
- PMID: 20015986
- PMCID: PMC2820919
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01388-09
ICP27 phosphorylation site mutants display altered functional interactions with cellular export factors Aly/REF and TAP/NXF1 but are able to bind herpes simplex virus 1 RNA
Abstract
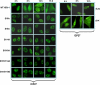
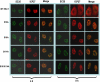
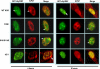
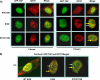
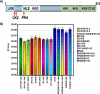
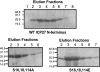
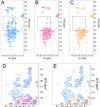
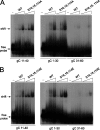
Herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) protein ICP27 is a multifunctional regulatory protein that is phosphorylated. Phosphorylation can affect protein localization, protein interactions, and protein function. The major sites of ICP27 that are phosphorylated are serine residues 16 and 18, within a CK2 site adjacent to a leucine-rich region required for ICP27 export, and serine 114, within a PKA site in the nuclear localization signal. Viral mutants bearing serine-to-alanine or glutamic acid substitutions at these sites are defective in viral replication and gene expression. To determine which interactions of ICP27 are impaired, we analyzed the subcellular localization of ICP27 and its colocalization with cellular RNA export factors Aly/REF and TAP/NXF1. In cells infected with phosphorylation site mutants, ICP27 was confined to the nucleus even at very late times after infection. ICP27 did not colocalize with Aly/REF or TAP/NXF1, and overexpression of TAP/NXF1 did not promote the export of ICP27 to the cytoplasm. However, in vitro binding experiments showed that mutant ICP27 was able to bind to the same RNA substrates as the wild type. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) analysis of the N terminus of ICP27 from amino acids 1 to 160, compared to mutants with triple substitutions to alanine or glutamic acid, showed that the mutations affected the overall conformation of the N terminus, such that mutant ICP27 was more flexible and unfolded. These results indicate that these changes in the structure of ICP27 altered in vivo protein interactions that occur in the N terminus but did not prevent RNA binding.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The cellular RNA export receptor TAP/NXF1 is required for ICP27-mediated export of herpes simplex virus 1 RNA, but the TREX complex adaptor protein Aly/REF appears to be dispensable.J Virol. 2009 Jul;83(13):6335-46. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00375-09. Epub 2009 Apr 15. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19369354 Free PMC article.
-
ICP27 recruits Aly/REF but not TAP/NXF1 to herpes simplex virus type 1 transcription sites although TAP/NXF1 is required for ICP27 export.J Virol. 2005 Apr;79(7):3949-61. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.7.3949-3961.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15767397 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient nuclear export of herpes simplex virus 1 transcripts requires both RNA binding by ICP27 and ICP27 interaction with TAP/NXF1.J Virol. 2009 Feb;83(3):1184-92. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02010-08. Epub 2008 Nov 19. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19019956 Free PMC article.
-
The many roles of the regulatory protein ICP27 during herpes simplex virus infection.Front Biosci. 2008 May 1;13:5241-56. doi: 10.2741/3078. Front Biosci. 2008. PMID: 18508584 Review.
-
Role of human herpesvirus homologs of infected cell protein 27 (ICP27) in the biogenesis, processing, and maturation of mRNAs.mBio. 2025 Apr 9;16(4):e0029125. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00291-25. Epub 2025 Mar 4. mBio. 2025. PMID: 40035535 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Herpesviridae Conserved Multifunctional Infected-Cell Protein 27 (ICP27) Is Important but Not Required for Replication and Oncogenicity of Marek's Disease Alphaherpesvirus.J Virol. 2019 Feb 5;93(4):e01903-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01903-18. Print 2019 Feb 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30518650 Free PMC article.
-
pUL69 of Human Cytomegalovirus Recruits the Cellular Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 6 via a Domain That Is Crucial for mRNA Export and Efficient Viral Replication.J Virol. 2015 Sep;89(18):9601-15. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01399-15. Epub 2015 Jul 15. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26178996 Free PMC article.
-
Host shutoff activity of VHS and SOX-like proteins: role in viral survival and immune evasion.Virol J. 2020 May 19;17(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s12985-020-01336-8. Virol J. 2020. PMID: 32430029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Herpes Simplex Virus-1 ICP27 Nuclear Export Signal Mutants Exhibit Cell Type-Dependent Deficits in Replication and ICP4 Expression.J Virol. 2023 Jul 27;97(7):e0195722. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01957-22. Epub 2023 Jun 13. J Virol. 2023. PMID: 37310267 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for the recognition of cellular mRNA export factor REF by herpes viral proteins HSV-1 ICP27 and HVS ORF57.PLoS Pathog. 2011 Jan 6;7(1):e1001244. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001244. PLoS Pathog. 2011. PMID: 21253573 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bachi, A., I. C. Braun, J. P. Rodrigues, N. Pante, K. Ribbeck, C. von Kobbe, U. Kutay, M. Wilm, D. Gorlich, M. Carmo-Fonseca, and E. Izaurralde. 2000. The C-terminal domain of TAP interacts with the nuclear pore complex and promotes export of specific CTE-bearing RNA substrates. RNA 6:136-158. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bedford, M. T., and S. Richard. 2005. Arginine methylation: an emerging regulator of protein function. Mol. Cell 18:263-272. - PubMed
-
- Bontems, S., E. De Valentin, L. Baudoux, B. Rentier, C. Sadzot-Delvaux, and J. Piette. 2002. Phosphorylation of varicella-zoster virus IE63 protein by casein kinases influences its cellular localization and gene regulation activity. J. Biol. Chem. 277:21050-21060. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

