HIV-1 Nef inhibits ruffles, induces filopodia, and modulates migration of infected lymphocytes
- PMID: 20015995
- PMCID: PMC2820911
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02230-09
HIV-1 Nef inhibits ruffles, induces filopodia, and modulates migration of infected lymphocytes
Abstract
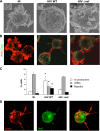
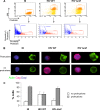
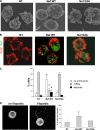
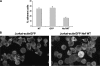
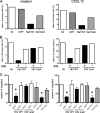
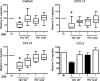
The HIV-1 Nef protein is a pathogenic factor modulating the behavior of infected cells. Nef induces actin cytoskeleton changes and impairs cell migration toward chemokines. We further characterized the morphology, cytoskeleton dynamics, and motility of HIV-1-infected lymphocytes. By using scanning electron microscopy, confocal immunofluorescence microscopy, and ImageStream technology, which combines flow cytometry and automated imaging, we report that HIV-1 induces a characteristic remodeling of the actin cytoskeleton. In infected lymphocytes, ruffle formation is inhibited, whereas long, thin filopodium-like protrusions are induced. Cells infected with HIV with nef deleted display a normal phenotype, and Nef expression alone, in the absence of other viral proteins, induces morphological changes. We also used an innovative imaging system to immobilize and visualize living individual cells in suspension. When combined with confocal "axial tomography," this technique greatly enhances three-dimensional optical resolution. With this technique, we confirmed the induction of long filopodium-like structures in unfixed Nef-expressing lymphocytes. The cytoskeleton reorganization induced by Nef is associated with an important impairment of cell movements. The adhesion and spreading of infected cells to fibronectin, their spontaneous motility, and their migration toward chemokines (CXCL12, CCL3, and CCL19) were all significantly decreased. Therefore, Nef induces complex effects on the lymphocyte actin cytoskeleton and cellular morphology, which likely impacts the capacity of infected cells to circulate and to encounter and communicate with bystander cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
HIV-1 Balances the Fitness Costs and Benefits of Disrupting the Host Cell Actin Cytoskeleton Early after Mucosal Transmission.Cell Host Microbe. 2019 Jan 9;25(1):73-86.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2018.12.008. Cell Host Microbe. 2019. PMID: 30629922 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 Nef disrupts the podocyte actin cytoskeleton by interacting with diaphanous interacting protein.J Biol Chem. 2008 Mar 28;283(13):8173-82. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M708920200. Epub 2008 Jan 30. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18234668 Free PMC article.
-
Massive secretion by T cells is caused by HIV Nef in infected cells and by Nef transfer to bystander cells.Cell Host Microbe. 2009 Sep 17;6(3):218-30. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2009.06.009. Cell Host Microbe. 2009. PMID: 19748464
-
The Contribution of Extracellular Nef to HIV-Induced Pathogenesis.Curr Drug Targets. 2016;17(1):46-53. doi: 10.2174/1389450116666151001110126. Curr Drug Targets. 2016. PMID: 26424397 Review.
-
Could Nef and Vpr proteins contribute to disease progression by promoting depletion of bystander cells and prolonged survival of HIV-infected cells?Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000 Jan 27;267(3):677-85. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1999.1708. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000. PMID: 10673351 Review.
Cited by
-
Subversion of the actin cytoskeleton during viral infection.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011 Jun;9(6):427-39. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2574. Epub 2011 Apr 27. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21522191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HIV-1 Nef Targets HDAC6 to Assure Viral Production and Virus Infection.Front Microbiol. 2019 Oct 30;10:2437. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02437. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31736889 Free PMC article.
-
LIM kinase 1 - dependent cofilin 1 pathway and actin dynamics mediate nuclear retinoid receptor function in T lymphocytes.BMC Mol Biol. 2011 Sep 16;12:41. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-12-41. BMC Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21923909 Free PMC article.
-
Efficiency of cell-free and cell-associated virus in mucosal transmission of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and simian immunodeficiency virus.J Virol. 2013 Dec;87(24):13589-97. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03108-12. Epub 2013 Oct 9. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 24109227 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 Nef and Vpu are functionally redundant broad-spectrum modulators of cell surface receptors, including tetraspanins.J Virol. 2014 Dec;88(24):14241-57. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02333-14. Epub 2014 Oct 1. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 25275127 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balabanian, K., J. Harriague, C. Decrion, B. Lagane, S. Shorte, F. Baleux, J. L. Virelizier, F. Arenzana-Seisdedos, and L. A. Chakrabarti. 2004. CXCR4-tropic HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein functions as a viral chemokine in unstimulated primary CD4+ T lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 173:7150-7160. - PubMed
-
- Ballestrem, C., B. Wehrle-Haller, and B. A. Imhof. 1998. Actin dynamics in living mammalian cells. J. Cell Sci. 111:1649-1658. - PubMed
-
- Baur, A. S., G. Sass, B. Laffert, D. Willbold, C. Cheng-Mayer, and B. M. Peterlin. 1997. The N-terminus of Nef from HIV-1/SIV associates with a protein complex containing Lck and a serine kinase. Immunity 6:283-291. - PubMed
-
- Bleul, C. C., M. Farzan, H. Choe, C. Parolin, Y. Clarck-Lewis, J. Sodroski, and T. A. Springer. 1996. The lymphocyte chemo-attractant SDF-1 is a ligand for lestr/fusin and blocks HIV-1 entry. Nature 382:829-833. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

