Two isoforms of Npap60 (Nup50) differentially regulate nuclear protein import
- PMID: 20016008
- PMCID: PMC2820426
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e09-05-0374
Two isoforms of Npap60 (Nup50) differentially regulate nuclear protein import
Abstract
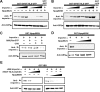
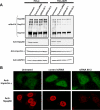
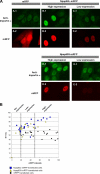
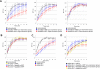
Npap60 (Nup50) is a nucleoporin that binds directly to importin alpha. In humans, there are two Npap60 isoforms: the long (Npap60L) and short (Npap60S) forms. In this study, we provide both in vitro and in vivo evidence that Npap60L and Npap60S function differently in nuclear protein import. In vitro binding assays revealed that Npap60S stabilizes the binding of importin alpha to classical NLS-cargo, whereas Npap60L promotes the release of NLS-cargo from importin alpha. In vivo time-lapse experiments showed that when the Npap60 protein level is controlled, allowing CAS to efficiently promote the dissociation of the Npap60/importin alpha complex, Npap60S and Npap60L suppress and accelerate the nuclear import of NLS-cargo, respectively. These results demonstrate that Npap60L and Npap60S have opposing functions and suggest that Npap60L and Npap60S levels must be carefully controlled for efficient nuclear import of classical NLS-cargo in humans. This study provides novel evidence that nucleoporin expression levels regulate nuclear import efficiency.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Npap60/Nup50 is a tri-stable switch that stimulates importin-alpha:beta-mediated nuclear protein import.Cell. 2002 Aug 9;110(3):349-60. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00836-x. Cell. 2002. PMID: 12176322
-
Nup50/Npap60 function in nuclear protein import complex disassembly and importin recycling.EMBO J. 2005 Nov 2;24(21):3681-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600843. Epub 2005 Oct 13. EMBO J. 2005. PMID: 16222336 Free PMC article.
-
The nucleoporin Nup358/RanBP2 promotes nuclear import in a cargo- and transport receptor-specific manner.Traffic. 2012 Feb;13(2):218-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2011.01302.x. Epub 2011 Nov 21. Traffic. 2012. PMID: 21995724
-
Npap60: a new player in nuclear protein import.Trends Cell Biol. 2003 Feb;13(2):61-4. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(02)00044-2. Trends Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12559755 Review.
-
Classical nuclear localization signals: definition, function, and interaction with importin alpha.J Biol Chem. 2007 Feb 23;282(8):5101-5. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R600026200. Epub 2006 Dec 14. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17170104 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of nucleocytoplasmic transport in skeletal muscle.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2011;96:273-302. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385940-2.00010-3. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 21621074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The nucleoporin Nup50 activates the Ran guanine nucleotide exchange factor RCC1 to promote NPC assembly at the end of mitosis.EMBO J. 2021 Dec 1;40(23):e108788. doi: 10.15252/embj.2021108788. Epub 2021 Nov 2. EMBO J. 2021. PMID: 34725842 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoblastoma-binding Protein 4-regulated Classical Nuclear Transport Is Involved in Cellular Senescence.J Biol Chem. 2015 Dec 4;290(49):29375-88. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.681908. Epub 2015 Oct 21. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26491019 Free PMC article.
-
TMEM160 Promotes Tumor Growth in Lung Adenocarcinoma and Cervical Adenocarcinoma Cell Lines.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 27;26(3):1097. doi: 10.3390/ijms26031097. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39940865 Free PMC article.
-
Micronutrient supplementation affects DNA methylation in male gonads with potential intergenerational epigenetic inheritance involving the embryonic development through glutamate receptor-associated genes.BMC Genomics. 2022 Feb 10;23(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08348-4. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35144563 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bayliss R., Littlewood T., Stewart M. Structural basis for the interaction between FxFG nucleoporin repeats and importin-beta in nuclear trafficking. Cell. 2000;102:99–108. - PubMed
-
- Chook Y. M., Blobel G. Karyopherins and nuclear import. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2001;11:703–715. - PubMed
-
- Fan F., Liu C. P., Korobova O., Heyting C., Offenberg H. H., Trump G., Arnheim N. cDNA cloning and characterization of Npap60, a novel rat nuclear pore-associated protein with an unusual subcellular localization during male germ cell differentiation. Genomics. 1997;40:444–453. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

