Comprehensive and rapid real-time PCR analysis of 21 foodborne outbreaks
- PMID: 20016673
- PMCID: PMC2775201
- DOI: 10.1155/2009/917623
Comprehensive and rapid real-time PCR analysis of 21 foodborne outbreaks
Abstract
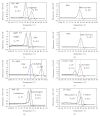
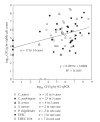
A set of four duplex SYBR Green I PCR (SG-PCR) assay combined with DNA extraction using QIAamp DNA Stool Mini kit was evaluated for the detection of foodborne bacteria from 21 foodborne outbreaks. The causative pathogens were detected in almost all cases in 2 hours or less. The first run was for the detection of 8 main foodborne pathogens in 5 stool specimens within 2 hours and the second run was for the detection of other unusual suspect pathogens within a further 45 minutes. After 2 to 4 days, the causative agents were isolated and identified. The results proved that for comprehensive and rapid molecular diagnosis in foodborne outbreaks, Duplex SG-PCR assay is not only very useful, but is also economically viable for one-step differentiation of causative pathogens in fecal specimens obtained from symptomatic patients. This then allows for effective diagnosis and management of foodborne outbreaks.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Simultaneous Screening of 24 Target Genes of Foodborne Pathogens in 35 Foodborne Outbreaks Using Multiplex Real-Time SYBR Green PCR Analysis.Int J Microbiol. 2010;2010:864817. doi: 10.1155/2010/864817. Epub 2010 Sep 28. Int J Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20936159 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of two methods of bacterial DNA extraction from human fecal samples contaminated with Clostridium perfringens, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella Typhimurium, and Campylobacter jejuni.Jpn J Infect Dis. 2014;67(6):441-6. doi: 10.7883/yoken.67.441. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 25410559
-
Duplex real-time SYBR green PCR assays for detection of 17 species of food- or waterborne pathogens in stools.J Clin Microbiol. 2003 Nov;41(11):5134-46. doi: 10.1128/JCM.41.11.5134-5146.2003. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 14605150 Free PMC article.
-
Advances and Challenges in Viability Detection of Foodborne Pathogens.Front Microbiol. 2016 Nov 22;7:1833. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01833. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27920757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic analysis of sapoviruses detected in outbreaks and sporadic cases of acute gastroenteritis in Miyagi Prefecture, Japan.J Clin Virol. 2020 Nov;132:104648. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104648. Epub 2020 Sep 19. J Clin Virol. 2020. PMID: 33038625
Cited by
-
Simultaneous Screening of 24 Target Genes of Foodborne Pathogens in 35 Foodborne Outbreaks Using Multiplex Real-Time SYBR Green PCR Analysis.Int J Microbiol. 2010;2010:864817. doi: 10.1155/2010/864817. Epub 2010 Sep 28. Int J Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20936159 Free PMC article.
-
Plesiomonas shigelloides Revisited.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2016 Apr;29(2):349-74. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00103-15. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2016. PMID: 26960939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploiting Bacterial Whole-Genome Sequencing Data for Evaluation of Diagnostic Assays: Campylobacter Species Identification as a Case Study.J Clin Microbiol. 2016 Dec;54(12):2882-2890. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01522-16. Epub 2016 Oct 12. J Clin Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27733632 Free PMC article.
-
SYBR®Green qPCR Salmonella detection system allowing discrimination at the genus, species and subspecies levels.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013 Nov;97(22):9811-24. doi: 10.1007/s00253-013-5234-x. Epub 2013 Oct 11. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 24113820 Free PMC article.
-
Detection and discrimination of five E. coli pathotypes using a combinatory SYBR® Green qPCR screening system.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 Apr;102(7):3267-3285. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-8820-0. Epub 2018 Feb 20. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29460001 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abubakar I, Irvine L, Aldus CF, et al. A systematic review of the clinical, public health and cost-effectiveness of rapid diagnostic tests for the detection and identification of bacterial intestinal pathogens in faeces and food. Health Technology Assessment. 2007;11(36):1–216. - PubMed
-
- Mackay IM. Real-time PCR in the microbiology laboratory. Clinical Microbiology and Infection. 2004;10(3):190–212. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

