Molecular Typing of Neisseria gonorrhoeae Isolates by Opa-Typing and Ribotyping in New Delhi, India
- PMID: 20016674
- PMCID: PMC2775202
- DOI: 10.1155/2009/934823
Molecular Typing of Neisseria gonorrhoeae Isolates by Opa-Typing and Ribotyping in New Delhi, India
Abstract
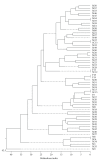
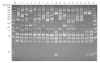
Control and preventive measures for gonococcal infections are based on precise epidemiological characteristics of N. gonorrhoeae isolates. In the present study the potential utility of opa-typing and ribotyping for molecular epidemiological study of consecutive gonococcal strains was determined. Sixty gonococcal isolates were subjected to ribotyping with two restriction enzymes, AvaII and HincII, and opa-typing with TaqI and HpaII for epidemiological characterization of gonococcal population. Ribotyping with AvaII yielded 6 ribotype patterns while twelve RFLP patterns were observed with HincII. Opa-typing of the 60 isolates revealed a total 54 opa-types, which 48 were unique and 6 formed clusters. Fifty-two opa-types were observed with TaqI-digested PCR product while opa-typing with HpaII demonstrated 54 opa-types. The opa-types from isolates that were epidemiologically unrelated were distinct, whereas those from the sexual contacts were identical. The results showed that opa-typing is highly useful for characterizing gonococcal strains from sexual contacts and has more discriminatory than ribotyping that could differentiate between gonococci of the same ribotype. The technique even with a single restriction enzyme has a high level of discrimination (99.9%) between epidemiologically unrelated isolates. In conclusion, the molecular methods such as opa-typing and ribotyping can be used for epidemiological characterization of gonococcal strains.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The diversity of the opa gene in gonococcal isolates from men who have sex with men.Sex Transm Infect. 2004 Aug;80(4):286-8. doi: 10.1136/sti.2003.006775. Sex Transm Infect. 2004. PMID: 15295127 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of sequencing of the por gene and typing of the opa gene for discrimination of Neisseria gonorrhoeae strains from sexual contacts.J Clin Microbiol. 2000 Dec;38(12):4430-8. doi: 10.1128/JCM.38.12.4430-4438.2000. J Clin Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 11101576 Free PMC article.
-
Concordance between Neisseria gonorrhoeae genotypes recovered from known sexual contacts.J Clin Microbiol. 2007 Nov;45(11):3564-7. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01453-07. Epub 2007 Sep 12. J Clin Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17855579 Free PMC article.
-
A prospective social and molecular investigation of gonococcal transmission.Lancet. 2000 Nov 25;356(9244):1812-7. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)03234-7. Lancet. 2000. PMID: 11117914
-
Opa-typing: a high-resolution tool for studying the epidemiology of gonorrhoea.Mol Microbiol. 1995 Sep;17(5):865-75. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.mmi_17050865.x. Mol Microbiol. 1995. PMID: 8596436
Cited by
-
Antimicrobial susceptibility and genetic characteristics of Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates from India, Pakistan and Bhutan in 2007-2011.BMC Infect Dis. 2013 Jan 24;13:35. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-13-35. BMC Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 23347339 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Analysis of Matched Isolates from Localized and Disseminated Gonococcal Infections Suggests That Opa Expression Impacts Clinical Outcome.Pathogens. 2022 Feb 7;11(2):217. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11020217. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 35215160 Free PMC article.
-
Review and international recommendation of methods for typing neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates and their implications for improved knowledge of gonococcal epidemiology, treatment, and biology.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2011 Jul;24(3):447-58. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00040-10. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21734242 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Invasive potential of nonencapsulated disease isolates of Neisseria meningitidis.Infect Immun. 2012 Jul;80(7):2346-53. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00293-12. Epub 2012 Apr 16. Infect Immun. 2012. PMID: 22508859 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control. Special focus: Trends in Reportable Sexually Transmitted Diseases in the United States. 2004.
-
- Gerbase AC, Rowley JT, Mertens TE. Global epidemiology of sexually transmitted diseases. Lancet. 1998;351(supplement 3):2–4. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

