Structural basis for the aminoacid composition of proteins from halophilic archea
- PMID: 20016684
- PMCID: PMC2780699
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000257
Structural basis for the aminoacid composition of proteins from halophilic archea
Abstract
Proteins from halophilic organisms, which live in extreme saline conditions, have evolved to remain folded at very high ionic strengths. The surfaces of halophilic proteins show a biased amino acid composition with a high prevalence of aspartic and glutamic acids, a low frequency of lysine, and a high occurrence of amino acids with a low hydrophobic character. Using extensive mutational studies on the protein surfaces, we show that it is possible to decrease the salt dependence of a typical halophilic protein to the level of a mesophilic form and engineer a protein from a mesophilic organism into an obligate halophilic form. NMR studies demonstrate complete preservation of the three-dimensional structure of extreme mutants and confirm that salt dependency is conferred exclusively by surface residues. In spite of the statistically established fact that most halophilic proteins are strongly acidic, analysis of a very large number of mutants showed that the effect of salt on protein stability is largely independent of the total protein charge. Conversely, we quantitatively demonstrate that halophilicity is directly related to a decrease in the accessible surface area.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
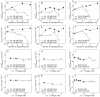
 or the msalt values for wild type proteins. A negative msalt value means that the cosolute destabilizes the protein.
or the msalt values for wild type proteins. A negative msalt value means that the cosolute destabilizes the protein.
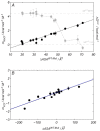
 , mKCl, and mNaCl) versus the number of substituted residues in the lysine involving mutations (n in XYxnWZ). For each panel, proteins and mutation classes are specified in the enclosed legend. Error bars result from propagation of the experimental uncertainties in the Tm values, by Montecarlo analysis. Dashed and dotted lines represent the
, mKCl, and mNaCl) versus the number of substituted residues in the lysine involving mutations (n in XYxnWZ). For each panel, proteins and mutation classes are specified in the enclosed legend. Error bars result from propagation of the experimental uncertainties in the Tm values, by Montecarlo analysis. Dashed and dotted lines represent the  or the mNaCl and mKCl for wild type ProtL, Hv 1A LigN, and Ec 1ALigN. A negative msalt value means that the cosolute destabilizes the protein.
or the mNaCl and mKCl for wild type ProtL, Hv 1A LigN, and Ec 1ALigN. A negative msalt value means that the cosolute destabilizes the protein.
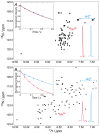
 , blue) nitrogen nuclei (inset of panel A) indicates fast tumbling of the polypeptide chain, a feature of unfolded proteins. Upon addition of salt (2 M NaCl), the peak pattern in the spectrum expands (B) and the T
2(15
N) of the main chain and the side chains can be discriminated (inset of panel B), as expected for a folded protein of this size. The same trend is manifested in the peak intensities of the HSQC spectra and the traces for the considered peaks are also shown in the bottom right-hand corners of the spectra. Solid lines in the figure insets correspond to the best exponential fitting to the experimental data (filled circles).
, blue) nitrogen nuclei (inset of panel A) indicates fast tumbling of the polypeptide chain, a feature of unfolded proteins. Upon addition of salt (2 M NaCl), the peak pattern in the spectrum expands (B) and the T
2(15
N) of the main chain and the side chains can be discriminated (inset of panel B), as expected for a folded protein of this size. The same trend is manifested in the peak intensities of the HSQC spectra and the traces for the considered peaks are also shown in the bottom right-hand corners of the spectra. Solid lines in the figure insets correspond to the best exponential fitting to the experimental data (filled circles).Similar articles
-
The crystal structure of Haloferax volcanii proliferating cell nuclear antigen reveals unique surface charge characteristics due to halophilic adaptation.BMC Struct Biol. 2009 Aug 22;9:55. doi: 10.1186/1472-6807-9-55. BMC Struct Biol. 2009. PMID: 19698123 Free PMC article.
-
Structural features of halophilicity derived from the crystal structure of dihydrofolate reductase from the Dead Sea halophilic archaeon, Haloferax volcanii.Structure. 1998 Jan 15;6(1):75-88. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(98)00009-4. Structure. 1998. PMID: 9493269
-
Halophilic to mesophilic adaptation of ubiquitin-like proteins.FEBS Lett. 2021 Feb;595(4):521-531. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.14023. Epub 2020 Dec 19. FEBS Lett. 2021. PMID: 33301612
-
Unique Features of Halophilic Proteins.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2017;18(1):65-71. doi: 10.2174/1389203717666160617111140. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2017. PMID: 27320124 Review.
-
Haloferax volcanii for biotechnology applications: challenges, current state and perspectives.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Feb;104(4):1371-1382. doi: 10.1007/s00253-019-10314-2. Epub 2019 Dec 20. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 31863144 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Marine extremophiles: a source of hydrolases for biotechnological applications.Mar Drugs. 2015 Apr 3;13(4):1925-65. doi: 10.3390/md13041925. Mar Drugs. 2015. PMID: 25854643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic basis of environmental adaptation in the widespread poly-extremophilic Exiguobacterium group.ISME J. 2024 Jan 8;18(1):wrad020. doi: 10.1093/ismejo/wrad020. ISME J. 2024. PMID: 38365240 Free PMC article.
-
Protein adaptations in archaeal extremophiles.Archaea. 2013;2013:373275. doi: 10.1155/2013/373275. Epub 2013 Sep 16. Archaea. 2013. PMID: 24151449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel mercuric reductase from the unique deep brine environment of Atlantis II in the Red Sea.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jan 17;289(3):1675-87. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.493429. Epub 2013 Nov 26. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24280218 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal Structure and Active Site Engineering of a Halophilic γ-Carbonic Anhydrase.Front Microbiol. 2020 Apr 28;11:742. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00742. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32411108 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pieper U, Kapadia G, Mevarech M, Herzberg O. Structural features of halophilicity derived from the crystal structure of dihydrofolate reductase from the Dead Sea halophilic archaeon, Haloferax volcanii. Structure. 1998;6:75–88. - PubMed
-
- Madern D, Ebel C, Zaccai G. Halophilic adaptation of enzymes. Extremophiles. 2000;4:91–98. - PubMed
-
- Mevarech M, Frolow F, Gloss L. M. Halophilic enzymes: proteins with a grain of salt. Biophys Chem. 2000;86:155–164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

