Meeting the Challenges of Neuroimaging Genetics
- PMID: 20016769
- PMCID: PMC2794202
- DOI: 10.1007/s11682-008-9029-0
Meeting the Challenges of Neuroimaging Genetics
Abstract
As research encompassing neuroimaging and genetics gains momentum, extraordinary information will be uncovered on the genetic architecture of the human brain. However, there are significant challenges to be addressed first. Not the least of these challenges is to accomplish the sample size necessary to detect subtle genetic influences on the morphometry and function of the healthy brain. Aside from sample size, image acquisition and analysis methods need to be refined in order to ensure optimum sensitivity to genetic and complementary environmental influences. Then there is the vexing issue of interpreting the resulting data. We describe how researchers from the east coast of Australia and the west coast of America have embarked upon a collaboration to meet these challenges using data currently being collected from a large-scale twin study, and offer some opinions about future directions in the field.
Figures
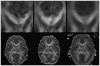

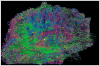
References
-
- Blokland GA, McMahon KL, Hoffman J, Zhu G, Meredith M, Martin NG, Thompson PM, de Zubicaray GI, Wright MJ. Quantifying the heritability of task-related brain activation and performance during the N-back working memory task: a twin fMRI study. 2008 doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2008.03.006. in press. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chiang M-C, Barysheva M, Lee AD, Madsen SK, Klunder AD, Toga AW, McMahon KL, de Zubicaray GI, Meredith M, Wright MJ, Srivastava A, Balov N, Thompson PM. Mapping genetic influences on brain fiber architecture with high angular resolution diffusion imaging (HARDI). 5th IEEE Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2008); 2008. pp. 871–874.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
