Protection of Salvia miltiorrhizae to the spleen and thymus of rats with severe acute pancreatitis or obstructive jaundice
- PMID: 20016826
- PMCID: PMC2790077
- DOI: 10.1155/2009/186136
Protection of Salvia miltiorrhizae to the spleen and thymus of rats with severe acute pancreatitis or obstructive jaundice
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the therapeutic effects and mechanism of Salvia miltiorrhizae in the treatment of SAP and OJ.
Methods: A total of 288 rats were used for SAP- and OJ-associated experiments. The rats were randomly divided into sham-operated group, model control group and treated group. The mortality rates of rats, contents of endotoxin and PLA(2) in blood, pathological changes of different indexes in spleen and thymus were observed.
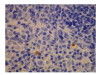
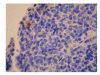
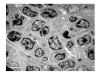
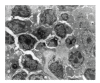
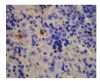
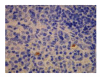
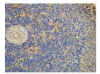
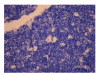
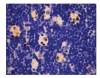
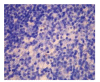
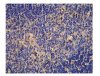
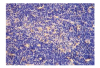
Results: The contents of endotoxin and PLA2 in treated group were significantly lower than those in model control group.The pathological severity scores of spleen and thymus of SAP rats as well as that of spleen of OJ rats in treated groups were significantly lower than those in model control groups (P < .05). The staining intensity as well as the product of the staining intensity and positive rate of Bax protein of spleen in model control group were significantly higher than those in treated groups (P < .01) , and the apoptosis index of spleen in treated group was significantly lower than that in model control group (P < .01).
Conclusion: Salvia miltiorrhizae exerts protective effects on the spleen and thymus of SAP rats and spleen of OJ rats.
Figures

References
-
- Miyazaki Y, Imamura H, Furukawa H, et al. A case of advanced gastric cancer with obstructive jaundice due to liver metastases successfully treated with chemotherapy. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2007;34(12):2132–2134. - PubMed
-
- Fuentes-Orozco C, Cervantes-Guevara G, Muciño-Hernández I, et al. L-alanyl-L-glutamine-supplemented parenteral nutrition decreases infectious morbidity rate in patients with severe acute pancreatitis. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition. 2008;32(4):403–411. - PubMed
-
- Rau BM, Bothe A, Kron M, Beger HG. Role of early multisystem organ failure as major risk factor for pancreatic infections and death in severe acute pancreatitis. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 2006;4(8):1053–1061. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Q, Ni Q, Cai D, Zhang Y, Zhang N, Hou L. Mechanisms of multiple organ damages in acute necrotizing pancreatitis. Chinese Medical Journal. 2001;114(7):738–742. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

