CLE peptide signaling during plant development
- PMID: 20016993
- PMCID: PMC2841256
- DOI: 10.1007/s00709-009-0095-y
CLE peptide signaling during plant development
Abstract
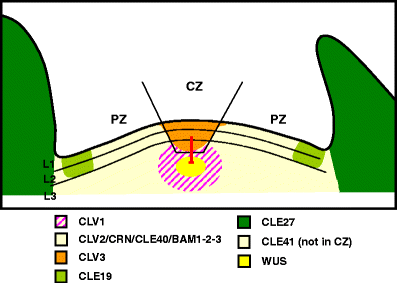
Peptide signaling in plants is a rapid developing area of research which focuses on so called peptide hormones. These signaling molecules are utilized for inter-cellular communication in different developmental processes, beside the usage of the more well-known phytohormones. Probably the best studied peptide ligands in plants are the CLAVATA3 (CLV3)/ENDOSPERM SURROUNDING REGION (ESR)-related (CLE) proteins. This family of signaling polypeptides is comprised of 32 members in Arabidopsis and, with the exception of the presence of related proteins in some parasitic worms, is restricted to the plant kingdom. CLV3 is one of the founding CLE genes and is involved in stem cell niche maintenance in apical meristems during plant development. While the CLV signaling pathway is well characterized with the identification of three receptors and a stem-cell-promoting transcription factor as target, the functioning of other family members is not or poorly understood. The recent discoveries of a new type of receptor involved in CLV signaling and a functional pathway for CLE40 in root development mark the rapid progress that is made in the area of CLE peptide signaling. This review gives an overview how CLE peptides are used as signaling molecules, and how they are involved in cell-to-cell communication in concert with different known and unknown receptors in a range of developmental processes during plant development.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Gain-of-function phenotypes of many CLAVATA3/ESR genes, including four new family members, correlate with tandem variations in the conserved CLAVATA3/ESR domain.Plant Physiol. 2006 Apr;140(4):1331-44. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.075515. Epub 2006 Feb 17. Plant Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16489133 Free PMC article.
-
Functional analysis of the cotton CLE polypeptide signaling gene family in plant growth and development.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 3;11(1):5060. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-84312-8. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33658526 Free PMC article.
-
CLE peptide signaling in plants - the power of moving around.Physiol Plant. 2015 Sep;155(1):74-87. doi: 10.1111/ppl.12358. Epub 2015 Jul 23. Physiol Plant. 2015. PMID: 26096704 Review.
-
Loss of CLE40, a protein functionally equivalent to the stem cell restricting signal CLV3, enhances root waving in Arabidopsis.Dev Genes Evol. 2003 Aug;213(8):371-81. doi: 10.1007/s00427-003-0329-5. Epub 2003 May 13. Dev Genes Evol. 2003. PMID: 12743822
-
CLE signaling systems during plant development and nematode infection.Plant Cell Physiol. 2012 Dec;53(12):1989-99. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcs136. Epub 2012 Oct 8. Plant Cell Physiol. 2012. PMID: 23045524 Review.
Cited by
-
An evolutionarily conserved pseudokinase mediates stem cell production in plants.Plant Cell. 2011 Mar;23(3):851-4. doi: 10.1105/tpc.110.075622. Epub 2011 Mar 11. Plant Cell. 2011. PMID: 21398569 Free PMC article.
-
Small signaling peptides in Arabidopsis development: how cells communicate over a short distance.Plant Cell. 2012 Aug;24(8):3198-217. doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.099010. Epub 2012 Aug 28. Plant Cell. 2012. PMID: 22932676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Database mining of plant peptide homologues.Plant Biotechnol (Tokyo). 2021 Mar 25;38(1):137-143. doi: 10.5511/plantbiotechnology.20.0720a. Plant Biotechnol (Tokyo). 2021. PMID: 34177333 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of putative CLE peptide receptors involved in determinate nodulation on soybean.Plant Signal Behav. 2011 Jul;6(7):1019-23. doi: 10.4161/psb.6.7.15575. Plant Signal Behav. 2011. PMID: 22004999 Free PMC article.
-
Peptide hormones in plants.Mol Hortic. 2025 Jan 23;5(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s43897-024-00134-y. Mol Hortic. 2025. PMID: 39849641 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

