Analysis of endogenous glutathione-adducts and their metabolites
- PMID: 20017120
- PMCID: PMC3802536
- DOI: 10.1002/bmc.1374
Analysis of endogenous glutathione-adducts and their metabolites
Abstract
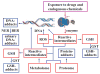
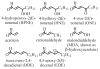
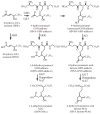
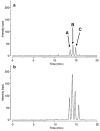
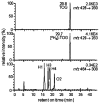
The ability to conduct validated analyses of glutathione (GSH)-adducts and their metabolites is critically important in order to establish whether they play a role in cellular biochemical or pathophysiological processes. The use of stable isotope dilution (SID) methodology in combination with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) provides the highest bioanalytical specificity possible for such analyses. Quantitative studies normally require the high sensitivity that can be obtained by the use of multiple reaction monitoring (MRM)/MS rather than the much less sensitive but more specific full scanning methodology. The method employs a parent ion corresponding to the intact molecule together with a prominent product ion that obtained by collision induced dissociation. Using SID LC-MRM/MS, analytes must have the same relative LC retention time to the heavy isotope internal standard established during the validation procedure, the correct parent ion and the correct product ion. This level of specificity cannot be attained with any other bioanalytical technique employed for biomarker analysis. This review will describe the application of SID LC-MR/MS methodology for the analysis of GSH-adducts and their metabolites. It will also discuss potential future directions for the use of this methodology for rigorous determination of their utility as disease and exposure biomarkers.
Figures


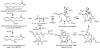


Similar articles
-
Stable-isotope dilution LC–MS for quantitative biomarker analysis.Bioanalysis. 2010 Feb;2(2):311-41. doi: 10.4155/bio.09.185. Bioanalysis. 2010. PMID: 20352077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Simultaneous determination of reduced glutathione, glutathione disulphide and glutathione sulphonamide in cells and physiological fluids by isotope dilution liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2009 Oct 15;877(28):3393-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2009.04.018. Epub 2009 Apr 15. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2009. PMID: 19414284
-
Cellular lipid extraction for targeted stable isotope dilution liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis.J Vis Exp. 2011 Nov 17;(57):3399. doi: 10.3791/3399. J Vis Exp. 2011. PMID: 22127066 Free PMC article.
-
An integrated approach for profiling oxidative metabolites and glutathione adducts using liquid chromatography coupled with ultraviolet detection and triple quadrupole-linear ion trap mass spectrometry.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2016 Sep 10;129:482-491. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2016.07.048. Epub 2016 Jul 30. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2016. PMID: 27497649
-
Androgen glucuronides analysis by liquid chromatography tandem-mass spectrometry: could it raise new perspectives in the diagnostic field of hormone-dependent malignancies?J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2013 Dec 1;940:24-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2013.09.022. Epub 2013 Sep 27. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 24140653 Review.
Cited by
-
Reactive metabolite production is a targetable liability of glycolytic metabolism in lung cancer.Nat Commun. 2019 Dec 6;10(1):5604. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13419-4. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31811141 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of New Chemical Tools against Leishmania amazonensis via the MMV Pathogen Box.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Nov 24;14(12):1219. doi: 10.3390/ph14121219. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34959620 Free PMC article.
-
Glutathione efflux and cell death.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012 Dec 15;17(12):1694-713. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.4553. Epub 2012 Jul 16. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012. PMID: 22656858 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glutathione conjugates of the mercapturic acid pathway and guanine adduct as biomarkers of exposure to CEES, a sulfur mustard analog.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2021 Feb;413(5):1337-1351. doi: 10.1007/s00216-020-03096-4. Epub 2021 Jan 7. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2021. PMID: 33410976
-
Stable-isotope dilution LC–MS for quantitative biomarker analysis.Bioanalysis. 2010 Feb;2(2):311-41. doi: 10.4155/bio.09.185. Bioanalysis. 2010. PMID: 20352077 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abrahim A, Al-Sayah M, Skrdla P, Bereznitski Y, Chen Y, Wu N. Practical comparison of 2.7 micron fused-core silica particles and porous sub-2 micron particles for fast separations in pharmaceutical process development. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis. 2010;51:131–137. - PubMed
-
- Alary J, Gueraud F, Cravedi JP. Fate of 4-hydroxynonenal in vivo: disposition and metabolic pathways. Molecular Aspects of Medicine. 2003;24:177–187. - PubMed
-
- Anders MW. Chemical toxicology of reactive intermediates formed by the glutathione-dependent bioactivation of halogen-containing compounds. Chemical Research in Toxicology. 2008;21:145–159. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong M, Liu AH, Harbeck R, Reisdorph R, Rabinovitch N, Reisdorph N. Leukotriene-E4 in human urine: comparison of on-line purification and liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry to affinity purification followed by enzyme immunoassay. Journal of Chromatography B Analytical Technologies in the Biomedical and Life Sciences. 2009;877:3169–3174. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

