Initial testing of topotecan by the pediatric preclinical testing program
- PMID: 20017204
- PMCID: PMC2923808
- DOI: 10.1002/pbc.22352
Initial testing of topotecan by the pediatric preclinical testing program
Abstract
Background: Topotecan is a small molecule DNA topoisomerase I poison, that has been successful in clinical trials against pediatric solid tumors and leukemias. Topotecan was evaluated against the Pediatric Preclinical Testing Program (PPTP) tumor panels as part of a validation process for these preclinical models.
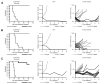
Procedures: In vivo three measures of antitumor activity were used: (1) an objective response measure modeled after the clinical setting; (2) a treated to control (T/C) tumor volume measure; and (3) a time to event (fourfold increase in tumor volume for solid tumor models, or > or =25% human CD45+ cells in the peripheral blood for acute lymphoblastic leukemia, ALL models) measure based on the median event-free survival (EFS) of treated and control animals for each xenograft.
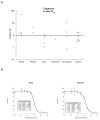
Results: Topotecan inhibited cell growth in vitro with IC(50) values between 0.71 and 489 nM. Topotecan significantly increased EFS in 32 of 37 (87%) solid tumor xenografts and in all 8 of the ALL xenografts. Seventy-five percent of solid tumors met EFS T/C activity criteria for intermediate (n = 17) or high activity (n = 7). Objective responses were noted in eight solid tumor xenografts (Wilms, rhabdomyosarcoma, Ewing sarcoma, neuroblastoma). Among the six neuroblastomas, three achieved a PR. For the ALL panel, two maintained CRs, three CRs, and two PRs were observed.
Conclusions: Topotecan demonstrated broad activity in vitro and in vivo against both the solid tumor and ALL panels, with significant tumor growth delay generated in all the panels. These results further demonstrate the validity of the PPTP panel for preclinical testing of new drugs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Comment in
-
Topotecan and etoposide combination to test neuroblastoma in pediatric preclinical testing program.Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2010 Aug;55(2):393. doi: 10.1002/pbc.22546. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20582962 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bomgaars L, Berg SL, Blaney SM. The Development of Camptothecin Analogs in Childhood Cancers. Oncologist. 2001;6(6):506–516. - PubMed
-
- Hsiang YH, Hertzberg R, Hecht S, et al. Camptothecin induces protein-linked DNA breaks via mammalian DNA topoisomerase I. J Biol Chem. 1985;260(27):14873–14878. - PubMed
-
- Hare CB, Elion GB, Houghton PJ, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of the topoisomerase I inhibitor 7-ethyl-10-(4-[1-piperidino]-1-piperidino)-carbonyloxy-camptothecin against pediatric and adult central nervous system tumor xenografts. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1997;39(3):187–191. - PubMed
-
- Pawlik CA, Houghton PJ, Stewart CF, et al. Effective schedules of exposure of medulloblastoma and rhabdomyosarcoma xenografts to topotecan correlate with in vitro assays. Clin Cancer Res. 1998;4(8):1995–2002. - PubMed
-
- Houghton PJ, Cheshire PJ, Hallman JD, 2nd, et al. Efficacy of topoisomerase I inhibitors, topotecan and irinotecan, administered at low dose levels in protracted schedules to mice bearing xenografts of human tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1995;36(5):393–403. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

