Molecular determinants for PP2A substrate specificity: charged residues mediate dephosphorylation of tyrosine hydroxylase by the PP2A/B' regulatory subunit
- PMID: 20017541
- PMCID: PMC3012350
- DOI: 10.1021/bi902160t
Molecular determinants for PP2A substrate specificity: charged residues mediate dephosphorylation of tyrosine hydroxylase by the PP2A/B' regulatory subunit
Abstract
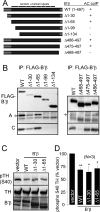
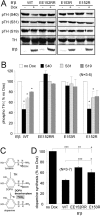
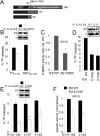
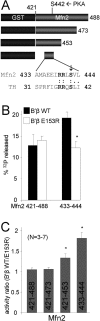
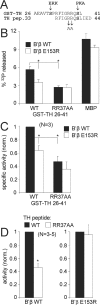
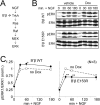
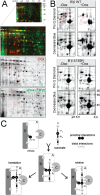
Together with protein phosphatase 1, protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) contributes the bulk of Ser/Thr phosphatase activity in most cell types. The predominant form of PP2A is a heterotrimer of catalytic (C), scaffolding (A), and diverse regulatory subunits (B, B', and B''). We have previously shown that N-terminal phosphorylation sites in tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), the rate-limiting enzyme in catecholamine synthesis, are specifically dephosphorylated by PP2A holoenzymes containing the B'beta regulatory subunit. Here, we identify a Glu residue conserved in B' regulatory subunits that is critical for dephosphorylation and inactivation of tyrosine hydroxylase in vitro and in PC12 cells. According to the PP2A heterotrimer crystal structure, Glu153 (B'beta numbering) abuts the catalytic site on the C subunit, and we demonstrate that Glu153 substitution inhibits multisite TH dephosphorylation without compromising PP2A/B'beta holoenzyme assembly or in vitro dephosphorylation of model substrates. Apart from its role in modulating TH activity, Glu153 is also necessary for PP2A/B'beta-mediated enhancement of nerve growth factor signaling. Furthermore, global phosphoproteome analysis suggests that Glu153 mediates dephosphorylation of most B'beta substrates in PC12 cells. With regard to selectivity determinants in the substrate, we show that B'beta Glu153 recognizes Arg37 and Arg38 in TH to direct dephosphorylation of both upstream (Ser31) and downstream (Ser40) sites. These results provide evidence of a subunit-spanning substrate docking site on the PP2A/B' holoenzyme, in which negatively charged side chains in the regulatory subunit interact with positive charges proximal to phosphorylated residues to mediate site-specific dephosphorylation.
Figures

References
-
- Hunter T. Protein kinases and phosphatases: The yin and yang of protein phosphorylation and signaling. Cell. 1995;80:225–236. - PubMed
-
- Janssens V, Longin S, Goris J. PP2A holoenzyme assembly: In cauda venenum (the sting is in the tail) Trends Biochem. Sci. 2008;33:113–121. - PubMed
-
- Virshup DM, Shenolikar S. From promiscuity to precision: Protein phosphatases get a makeover. Mol. Cell. 2009;33:537–545. - PubMed
-
- Strack S, Zaucha JA, Ebner FF, Colbran RJ, Wadzinski BE. Brain protein phosphatase 2A: Developmental regulation and distinct cellular and subcellular localization by B subunits. J. Comp. Neurol. 1998;392:515–527. - PubMed
-
- Dagda RK, Zaucha JA, Wadzinski BE, Strack S. A developmentally regulated, neuron-specific splice variant of the variable subunit Bβ targets protein phosphatase 2A to mitochondria and modulates apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:24976–24985. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

