Label-free fluorescent aptamer sensor based on regulation of malachite green fluorescence
- PMID: 20017558
- PMCID: PMC2821951
- DOI: 10.1021/ac9018473
Label-free fluorescent aptamer sensor based on regulation of malachite green fluorescence
Abstract
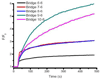
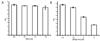
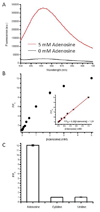
We report a label-free fluorescent aptamer sensor for adenosine based on the regulation of malachite green (MG) fluorescence, with comparable sensitivity and selectivity to other labeled adenosine aptamer-based sensors. The sensor consists of free MG, an aptamer strand containing an adenosine aptamer next to an MG aptamer, and a bridging strand that partially hybridizes to the aptamer strand. Such a hybridization prevents MG from binding to MG aptamer, resulting in low fluorescence of MG in the absence of adenosine. Addition of adenosine causes the adenosine aptamer to bind adenosine, weakening the hybridization of the aptamer strand with the bridging strand, making it possible for MG to bind to the aptamer strand and exhibit high fluorescence intensity. Since this design is based purely on nucleic acid hybridization, it can be generally applied to other aptamers for the label-free detection of a broad range of analytes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An enzyme-free strategy for ultrasensitive detection of adenosine using a multipurpose aptamer probe and malachite green.Anal Chim Acta. 2015 Aug 5;887:179-185. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2015.05.046. Epub 2015 Jul 8. Anal Chim Acta. 2015. PMID: 26320800
-
A simple and label-free sensor for mercury(II) detection in aqueous solution by malachite green based on a resonance scattering spectral assay.Chem Commun (Camb). 2011 Jun 7;47(21):6027-9. doi: 10.1039/c1cc10563a. Epub 2011 May 11. Chem Commun (Camb). 2011. PMID: 21559531
-
Abasic site-containing DNAzyme and aptamer for label-free fluorescent detection of Pb(2+) and adenosine with high sensitivity, selectivity, and tunable dynamic range.J Am Chem Soc. 2009 Oct 28;131(42):15352-7. doi: 10.1021/ja905854a. J Am Chem Soc. 2009. PMID: 19807110 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorescence generation from tandem repeats of a malachite green RNA aptamer using rolling circle transcription.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2008 Aug 15;18(16):4562-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2008.07.040. Epub 2008 Jul 15. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2008. PMID: 18667307
-
[A fluorescence method based on malachite green/aptamer for detection of ochratoxin A in traditional Chinese medicines].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024 Apr;49(7):1818-1825. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20240118.102. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38812194 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Aptamer-based fluorescent biosensors.Curr Med Chem. 2011;18(27):4175-84. doi: 10.2174/092986711797189637. Curr Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21838688 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent trends in SELEX technique and its application to food safety monitoring.Mikrochim Acta. 2014 Apr;181(5-6):479-491. doi: 10.1007/s00604-013-1156-7. Mikrochim Acta. 2014. PMID: 25419005 Free PMC article.
-
Highly sensitive optical biosensor for thrombin based on structure switching aptamer-luminescent silica nanoparticles.J Fluoresc. 2013 Jan;23(1):137-46. doi: 10.1007/s10895-012-1127-0. Epub 2012 Sep 11. J Fluoresc. 2013. PMID: 22965479
-
FaptaSyme: A Strategy for Converting a Monomer/Oligomer-Nonselective Aptameric Sensor into an Oligomer-Selective One.Chembiochem. 2018 Apr 26:10.1002/cbic.201800017. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201800017. Online ahead of print. Chembiochem. 2018. PMID: 29700982 Free PMC article.
-
Real-Time PCR-Coupled CE-SELEX for DNA Aptamer Selection.ISRN Mol Biol. 2012 Aug 8;2012:939083. doi: 10.5402/2012/939083. eCollection 2012. ISRN Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 27335672 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

