An overview of IL-7 biology and its use in immunotherapy
- PMID: 20017587
- PMCID: PMC2826542
- DOI: 10.3109/15476910903453296
An overview of IL-7 biology and its use in immunotherapy
Abstract
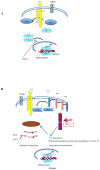
Interleukin (IL)-7 is required for T-cell development as well as for the survival and homeostasis of mature T-cells. In the thymus, the double negative (DN) CD4(-) CD8(-) thymocyte progenitor transition into double positive CD4+ CD8+ cells requires Notch and IL-7 signaling. Importantly, IL-7 seems to have a dose effect on T-cell development and, at high doses, DN progression is blocked. Naïve T-cells in the thymus, and after their exit to the periphery, are dependent on IL-7 and TCR signaling for survival. Upon antigen exposure, they proliferate and differentiate into memory T-cells. Because IL-7 intervenes at all stages of T-cell development and maintenance, it has been introduced recently into clinical trials as an immunotherapeutic agent for cancer patients (of particular note, those who had undergone T-cell depleting therapy) in an attempt to increase their population sizes of CD4+ and CD8+ cells overall, and specifically of CD8+ (CD45RA+)CCR7+ and/or CD27+), CD4+ (CD45RA+CD31+), and CD4+ central memory T-cells (CD45RA(-)CCR7+). Interestingly, IL-7 in humans induced a preferential expansion of naïve T-cells, resulting in a broader T-cell repertoire than before the treatment; this effect was independent of age. This suggests that IL-7 therapy could enhance immune responses in patients with limited naïve T-cell numbers as in aged patients or after disease-induced or iatrogenic T-cell depletion. This overview highlights the role of IL-7 on T-cells in mice and humans.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors report no conflicts of interest. The Authors are alone responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 stringently regulates distinct functions of IL-7 and IL-15 in vivo during T lymphocyte development and homeostasis.J Immunol. 2006 Apr 1;176(7):4029-41. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.7.4029. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16547238
-
Ongoing Dll4-Notch signaling is required for T-cell homeostasis in the adult thymus.Eur J Immunol. 2011 Aug;41(8):2207-16. doi: 10.1002/eji.201041343. Epub 2011 Jul 4. Eur J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21598246
-
Effect of IL-7 Therapy on Naive and Memory T Cell Homeostasis in Aged Rhesus Macaques.J Immunol. 2015 Nov 1;195(9):4292-305. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500609. Epub 2015 Sep 28. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26416281 Free PMC article.
-
Intrathymic IL-7: the where, when, and why of IL-7 signaling during T cell development.Semin Immunol. 2012 Jun;24(3):151-8. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2012.02.002. Epub 2012 Mar 14. Semin Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22421571 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytokine synergy in antigen-independent activation and priming of naive CD8+ T lymphocytes.Crit Rev Immunol. 2009;29(3):219-39. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.v29.i3.30. Crit Rev Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19538136 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting osteosarcoma with canine B7-H3 CAR T cells and impact of CXCR2 Co-expression on functional activity.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2024 Mar 30;73(5):77. doi: 10.1007/s00262-024-03642-4. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2024. PMID: 38554158 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant Signaling Pathways in T-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Sep 5;18(9):1904. doi: 10.3390/ijms18091904. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28872614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Application of Cytokines in Cancer Immunotherapy.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021 May 27;15:2269-2287. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S308578. eCollection 2021. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021. PMID: 34079226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism of Action of IL-7 and Its Potential Applications and Limitations in Cancer Immunotherapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 May 6;16(5):10267-80. doi: 10.3390/ijms160510267. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25955647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells directly participate in host immune response.Am J Stem Cells. 2021 Jun 15;10(2):18-27. eCollection 2021. Am J Stem Cells. 2021. PMID: 34327049 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akashi K, Kondo M, vonFreedenJeffry U, Murray R, Weissman IL. Bcl-2 rescues T lymphopoiesis in interleukin-7 receptor-deficient mice. Cell. 1997;89:1033–1041. - PubMed
-
- Allman D, Sambandam A, Kim S, Miller JP, Pagan A, Well D, Meraz A, Bhandoola A. Thymopoiesis independent of common lymphoid progenitors. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:168–174. - PubMed
-
- Baird AM, Lucas JA, Berg LJ. A profound deficiency in thymic progenitor cells in mice lacking Jak3. J Immunol. 2000;165:3680–3688. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
