Cellular and bacterial profiles associated with oral epithelium-microbiota interactions
- PMID: 20017802
- PMCID: PMC3087601
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0757.2009.00322.x
Cellular and bacterial profiles associated with oral epithelium-microbiota interactions
Figures
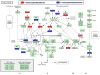
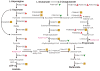
Similar articles
-
Periodontal microbial complexes associated with specific cell and tissue responses.J Clin Periodontol. 2011 Mar;38 Suppl 11:17-27. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2010.01668.x. J Clin Periodontol. 2011. PMID: 21323700 Review.
-
The interface between the mucosa and the implant.Periodontol 2000. 1998 Jun;17:47-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0757.1998.tb00122.x. Periodontol 2000. 1998. PMID: 10337312 Review. No abstract available.
-
The chronicles of Porphyromonas gingivalis: the microbium, the human oral epithelium and their interplay.Microbiology (Reading). 2008 Oct;154(Pt 10):2897-2903. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2008/021220-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2008. PMID: 18832296 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Models of oral and vaginal candidiasis based on in vitro reconstituted human epithelia for the study of host-pathogen interactions.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;470:327-45. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-204-5_23. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19089393
-
Distinct gene expression characteristics in epithelial cell-Porphyromonas gingivalis interactions by integrating transcriptome analyses.Int J Med Sci. 2019 Sep 7;16(10):1320-1327. doi: 10.7150/ijms.33728. eCollection 2019. Int J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31692996 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The oral microbiota: dynamic communities and host interactions.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2018 Dec;16(12):745-759. doi: 10.1038/s41579-018-0089-x. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30301974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bee Venom Inhibits Porphyromonas gingivalis Lipopolysaccharides-Induced Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines through Suppression of NF-κB and AP-1 Signaling Pathways.Molecules. 2016 Nov 10;21(11):1508. doi: 10.3390/molecules21111508. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27834922 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

