Interleukin-23 is critical for full-blown expression of a non-autoimmune destructive arthritis and regulates interleukin-17A and RORgammat in gammadelta T cells
- PMID: 20017902
- PMCID: PMC3003524
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2893
Interleukin-23 is critical for full-blown expression of a non-autoimmune destructive arthritis and regulates interleukin-17A and RORgammat in gammadelta T cells
Abstract
Introduction: Interleukin (IL)-23 is essential for the development of various experimental autoimmune models. However, the role of IL-23 in non-autoimmune experimental arthritis remains unclear. Here, we examined the role of IL-23 in the non-autoimmune antigen-induced arthritis (AIA) model. In addition, the regulatory potential of IL-23 in IL-17A and retinoic acid-related orphan receptor gamma t (RORgammat) expression in CD4+ and TCRgammadelta+ T cells was evaluated systemically as well as at the site of inflammation.
Methods: Antigen-induced arthritis was induced in wild-type, IL-23p19-deficient and IL-17 Receptor A - knockout mice. At different time points, synovial cytokine and chemokine expression was measured. At days 1 and 7 of AIA, splenocytes and joint-infiltrating cells were isolated and analyzed for intracellular IL-17A and interferon (IFN)-gamma ex-vivo by flow cytometry. In splenic CD4+ and TCRgammadelta+ T cells gene expression was quantified by flow cytometry and quantitative PCR.
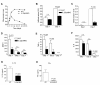
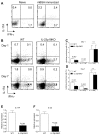
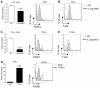
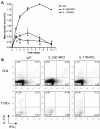
Results: IL-23 was critical for full-blown AIA. Lack of IL-23 did not prevent the onset of joint inflammation but stopped the progression to a destructive synovitis. IL-23 regulated IL-17A expression in CD4+ T cells in the spleen. Of note, IL-17A and IFN-gamma expression was reduced in CD4+ T cells in the inflamed joints of IL-23p19-deficient mice. Interestingly, IL-23 was also critical for the induction of IL-17A and RORgammat but not IFN-gamma in TCRgammadelta+ T cells in the inflamed joints. The importance of the IL-23/IL-17 axis was further confirmed using IL-17 Receptor A knockout mice showing significantly milder AIA compared to control mice, with a disease course comparable to that of IL-23p19-deficient mice.
Conclusions: These data show that IL-23 is critical for full-blown expression of a non-autoimmune destructive arthritis and regulates the proportion of IL-17A and IFN-gamma-positive CD4+ T cells at the site of inflammation. Furthermore, IL-23 regulates IL-17A and RORgammat expression in TCRgammadelta T cells in arthritis. These findings indicate that regulating the IL-23 pathway may have therapeutic potential in non-autoimmune arthritis.
Figures


References
-
- Oppmann B, Lesley R, Blom B, Timans JC, Xu Y, Hunte B, Vega F, Yu N, Wang J, Singh K, Zonin F, Vaisberg E, Churakova T, Liu M, Gorman D, Wagner J, Zurawski S, Liu Y, Abrams JS, Moore KW, Rennick D, de Waal-Malefyt R, Hannum C, Bazan JF, Kastelein RA. Novel p19 protein engages IL-12p40 to form a cytokine, IL-23, with biological activities similar as well as distinct from IL-12. Immunity. 2000;13:715–725. doi: 10.1016/S1074-7613(00)00070-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cua DJ, Sherlock J, Chen Y, Murphy CA, Joyce B, Seymour B, Lucian L, To W, Kwan S, Churakova T, Zurawski S, Wiekowski M, Lira SA, Gorman D, Kastelein RA, Sedgwick JD. Interleukin-23 rather than interleukin-12 is the critical cytokine for autoimmune inflammation of the brain. Nature. 2003;421:744–748. doi: 10.1038/nature01355. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

