Differential NR2B subunit expression at dorsal root and ventrolateral funiculus synapses on lumbar motoneurons of neonatal rat
- PMID: 20018230
- PMCID: PMC2823957
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.12.025
Differential NR2B subunit expression at dorsal root and ventrolateral funiculus synapses on lumbar motoneurons of neonatal rat
Abstract
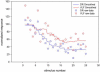
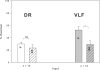
Synapse specific differences in NR2 subunit expression exist in several systems within the mammalian CNS. Here we have studied such differences on motoneurons in the neonatal rat cord using ifenprodil known to inhibit voltage-, use- and glycine-independent responses mediated by NR2B-containing N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) with high specificity. In neonatal rats (P1-P9), the synapses made by the dorsal root (DR) fibres were more sensitive to ifenprodil than ventrolateral funiculus (VLF) connections on the same motoneuron. DR connections exhibited very little additional blockade to bath-applied MK-801 whereas VLF connections displayed a further decrease in amplitude. This suggests that at this immediate postnatal age, DR synapses on motoneurons contain a higher proportion of ifenprodil-sensitive diheteromeric NR1/NR2B receptors than VLF synapses. Since DR synapses have been shown in other studies to be less mature than VLF synapses on the same motoneuron at this developmental stage, these data are interpreted as indicating that less mature NMDA receptors feature a higher proportion of NR2B subunits which declines as the synapse matures. This novel finding of staggered development of NMDA receptors from different synaptic inputs on the same motoneuron is discussed in the context of its developmental and functional implications.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Input-specific plasticity of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-mediated synaptic responses in neonatal rat motoneurons.Eur J Neurosci. 2009 Jun;29(11):2125-36. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.06769.x. Epub 2009 Jun 1. Eur J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19490018 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of metabotropic glutamate receptor responses at segmental and descending inputs to motoneurons in neonatal rat spinal cord.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005 Feb;312(2):669-77. doi: 10.1124/jpet.104.075077. Epub 2004 Sep 21. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005. PMID: 15383635
-
Acute modulation of synaptic transmission to motoneurons by BDNF in the neonatal rat spinal cord.Eur J Neurosci. 2001 Dec;14(11):1800-8. doi: 10.1046/j.0953-816x.2001.01811.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11860475
-
Synaptic transmission between ventrolateral funiculus axons and lumbar motoneurons in the isolated spinal cord of the neonatal rat.J Neurophysiol. 1994 Nov;72(5):2406-19. doi: 10.1152/jn.1994.72.5.2406. J Neurophysiol. 1994. PMID: 7884467
-
NT-3 evokes an LTP-like facilitation of AMPA/kainate receptor-mediated synaptic transmission in the neonatal rat spinal cord.J Neurophysiol. 2000 Aug;84(2):752-8. doi: 10.1152/jn.2000.84.2.752. J Neurophysiol. 2000. PMID: 10938302
Cited by
-
Distinct and developmentally regulated activity-dependent plasticity at descending glutamatergic synapses on flexor and extensor motoneurons.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 22;6:28522. doi: 10.1038/srep28522. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27329279 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arvanian VL, Mendell LM. Removal of NMDA receptor Mg(2+) block extends the action of NT-3 on synaptic transmission in neonatal rat motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 2001;86:123–129. - PubMed
-
- Arvanian VL, Bowers WJ, Petruska JC, Motin V, Manuzon H, Narrow WC, Federoff HJ, Mendell LM. Viral delivery of NR2D subunits reduces Mg2+ block of NMDA receptor and restores NT-3-induced potentiation of AMPA-kainate responses in maturing rat motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 2004;92:2394–2404. - PubMed
-
- Arvanov VL, Seebach BS, Mendell LM. NT-3 evokes an LTP-like facilitation of AMPA/kainate receptor-mediated synaptic transmission in the neonatal rat spinal cord. J Neurophysiol. 2000;84:752–758. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

