Trace and contextual fear conditioning is enhanced in mice lacking the alpha4 subunit of the GABA(A) receptor
- PMID: 20018248
- PMCID: PMC3985603
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nlm.2009.12.004
Trace and contextual fear conditioning is enhanced in mice lacking the alpha4 subunit of the GABA(A) receptor
Abstract
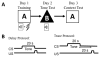
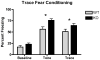
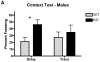
The GABA(A)R alpha4 subunit is highly expressed in the dentate gyrus region of the hippocampus at predominantly extra synaptic locations where, along with the GABA(A)R delta subunit, it forms GABA(A) receptors that mediate a tonic inhibitory current. The present study was designed to test hippocampus-dependent and hippocampus-independent learning and memory in GABA(A)R alpha4 subunit-deficient mice using trace and delay fear conditioning, respectively. Mice were of a mixed C57Bl/6J X 129S1/X1 genetic background from alpha4 heterozygous breeding pairs. The alpha4-knockout mice showed enhanced trace and contextual fear conditioning consistent with an enhancement of hippocampus-dependent learning and memory. These enhancements were sex-dependent, similar to previous studies in GABA(A)R delta knockout mice, but differences were present in both males and females. The convergent findings between alpha4 and delta knockout mice suggests that tonic inhibition mediated by alpha4betadelta GABA(A) receptors negatively modulates learning and memory processes and provides further evidence that tonic inhibition makes important functional contributions to learning and behavior.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
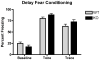

Similar articles
-
Behavioral pharmacogenetic analysis on the role of the α4 GABA(A) receptor subunit in the ethanol-mediated impairment of hippocampus-dependent contextual learning.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2011 Nov;35(11):1948-59. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2011.01546.x. Epub 2011 Sep 21. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2011. PMID: 21943327 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the δ GABA(A) receptor in ovarian cycle-linked changes in hippocampus-dependent learning and memory.Neurochem Res. 2014 Jun;39(6):1140-6. doi: 10.1007/s11064-014-1282-6. Epub 2014 Mar 26. Neurochem Res. 2014. PMID: 24667980
-
Trace fear conditioning is enhanced in mice lacking the delta subunit of the GABAA receptor.Learn Mem. 2005 May-Jun;12(3):327-33. doi: 10.1101/lm.89705. Epub 2005 May 16. Learn Mem. 2005. PMID: 15897254 Free PMC article.
-
Gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor alpha 4 subunit knockout mice are resistant to the amnestic effect of isoflurane.Anesth Analg. 2009 Dec;109(6):1816-22. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3181bf6ae6. Anesth Analg. 2009. PMID: 19923508 Free PMC article.
-
α4βδ GABAA receptors and tonic inhibitory current during adolescence: effects on mood and synaptic plasticity.Front Neural Circuits. 2013 Sep 3;7:135. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2013.00135. eCollection 2013. Front Neural Circuits. 2013. PMID: 24027497 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hippocampal metaplasticity is required for the formation of temporal associative memories.J Neurosci. 2014 Dec 10;34(50):16762-73. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2869-13.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25505329 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral outputs and overlapping circuits between conditional fear and active avoidance.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2024 Sep;213:107943. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2024.107943. Epub 2024 May 29. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2024. PMID: 38821256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sexual differentiation of contextual fear responses.Learn Mem. 2018 Apr 16;25(5):230-240. doi: 10.1101/lm.047159.117. Print 2018 May. Learn Mem. 2018. PMID: 29661835 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy alleviates vascular dysfunction and amyloid burden in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model and in elderly patients.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Sep 9;13(17):20935-20961. doi: 10.18632/aging.203485. Epub 2021 Sep 9. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34499614 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomics of Gabra4 knockout mice reveals common NMDAR pathways underlying autism, memory, and epilepsy.Mol Autism. 2020 Feb 7;11(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s13229-020-0318-9. Mol Autism. 2020. PMID: 32033586 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Belelli D, Lambert JJ. Neurosteroids: endogenous regulators of the GABA(A) receptor. Nature reviews. 2005;6:565–575. - PubMed
-
- Benke D, Michel C, Mohler H. GABA(A) receptors containing the alpha4 subunit: prevalence, distribution, pharmacology and subunit architecture in situ. Journal of Neurochemistry. 1997;69:806–814. - PubMed
-
- Bitran D, Dugan M, Renda P, Ellis R, Foley M. Anxiolytic effects of the neuroactive steroid pregnanolone (3 alpha-OH-5 beta-pregnan-20-one) after microinjection in the dorsal hippocampus and lateral septum. Brain Research. 1999;850:217–224. - PubMed
-
- Blanchard RJ, Blanchard DC, Weiss SM. Ethanol effects in an anxiety/defense test battery. Alcohol. 1990;7:375–381. - PubMed
-
- Boatman JA, Kim JJ. A thalamo-cortico-amygdala pathway mediates auditory fear conditioning in the intact brain. The European journal of neuroscience. 2006;24:894–900. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 MH062122/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DE014184/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH019384/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS035985/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA013004/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AA007680/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA007680/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- AA13004/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- DE14184/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- GM47818/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- AA07680/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P01NS35985/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 GM047818/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- NS35985/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

