Insulin-like actions of glucagon-like peptide-1: a dual receptor hypothesis
- PMID: 20018525
- PMCID: PMC4085161
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tem.2009.11.007
Insulin-like actions of glucagon-like peptide-1: a dual receptor hypothesis
Abstract
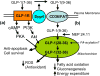
GLP-1 (9-36)amide is the cleavage product of GLP-1(7-36) amide, formed by the action of diaminopeptidyl peptidase-4 (Dpp4), and is the major circulating form in plasma. Whereas GLP-1(7-36)amide stimulates glucose-dependent insulin secretion, GLP-1(9-36)amide has only weak partial insulinotropic agonist activities on the GLP-1 receptor, but suppresses hepatic glucose production, exerts antioxidant cardioprotective actions and reduces oxidative stress in vasculature tissues. These insulin-like activities suggest a role for GLP-1 (9-36)amide in the modulation of mitochondrial functions by mechanisms independent of the GLP-1 receptor. In this paper, we discuss the current literature suggesting that GLP-1(9-36)amide is an active peptide with important insulin-like actions. These findings have implications in nutrient assimilation, energy homeostasis, obesity, and the use of Dpp4 inhibitors for the treatment of diabetes.
Copyright (c) 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
GLP-1 (9-36) amide metabolite suppression of glucose production in isolated mouse hepatocytes.Horm Metab Res. 2010 Aug;42(9):657-62. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1253421. Epub 2010 May 28. Horm Metab Res. 2010. PMID: 20645222
-
Glucagon-like peptide (GLP)-1(9-36)amide-mediated cytoprotection is blocked by exendin(9-39) yet does not require the known GLP-1 receptor.Endocrinology. 2010 Apr;151(4):1520-31. doi: 10.1210/en.2009-1197. Epub 2010 Feb 19. Endocrinology. 2010. PMID: 20172966
-
GLP-1 (9-36) amide, cleavage product of GLP-1 (7-36) amide, is a glucoregulatory peptide.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2008 Jul;16(7):1501-9. doi: 10.1038/oby.2008.229. Epub 2008 Apr 17. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2008. PMID: 18421270
-
Clinical review: The extrapancreatic effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 and related peptides.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009 Jun;94(6):1843-52. doi: 10.1210/jc.2008-1296. Epub 2009 Mar 31. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009. PMID: 19336511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (7-36) amide as a novel neuropeptide.Mol Neurobiol. 1998 Oct;18(2):157-73. doi: 10.1007/BF02914270. Mol Neurobiol. 1998. PMID: 10065878 Review.
Cited by
-
GLP-1RAs and cardiovascular disease: is the endothelium a relevant platform?Acta Diabetol. 2023 Nov;60(11):1441-1448. doi: 10.1007/s00592-023-02124-w. Epub 2023 Jul 4. Acta Diabetol. 2023. PMID: 37401947 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Beneficial Effects of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists Other than Their Anti-Diabetic and Anti-Obesity Properties.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Dec 26;61(1):17. doi: 10.3390/medicina61010017. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39858999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GLP-1(32-36)amide, a novel pentapeptide cleavage product of GLP-1, modulates whole body glucose metabolism in dogs.Peptides. 2014 Sep;59:20-4. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2014.06.004. Epub 2014 Jun 14. Peptides. 2014. PMID: 24937653 Free PMC article.
-
Cardioprotection Resulting from Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Administration Involves Shifting Metabolic Substrate Utilization to Increase Energy Efficiency in the Rat Heart.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 22;10(6):e0130894. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130894. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26098939 Free PMC article.
-
Vertical sleeve gastrectomy activates GPBAR-1/TGR5 to sustain weight loss, improve fatty liver, and remit insulin resistance in mice.Hepatology. 2016 Sep;64(3):760-73. doi: 10.1002/hep.28689. Epub 2016 Jul 25. Hepatology. 2016. PMID: 27312543 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kieffer TJ, Habener JF. The glucagon-like peptides. Endocr Rev. 1999;20:876–913. - PubMed
-
- Estall JL, Drucker DJ. Glucagon-like Peptide-2. Annu Rev Nutr. 2006;26:391–411. - PubMed
-
- Jiang G, Zhang BB. Glucagon and regulation of glucose metabolism. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2003;284:E671–678. - PubMed
-
- Lovshin JA, Drucker DJ. Incretin-based therapies for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2009;5:262–269. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

