Insulin-like actions of glucagon-like peptide-1: a dual receptor hypothesis
- PMID: 20018525
- PMCID: PMC4085161
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tem.2009.11.007
Insulin-like actions of glucagon-like peptide-1: a dual receptor hypothesis
Abstract
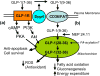
GLP-1 (9-36)amide is the cleavage product of GLP-1(7-36) amide, formed by the action of diaminopeptidyl peptidase-4 (Dpp4), and is the major circulating form in plasma. Whereas GLP-1(7-36)amide stimulates glucose-dependent insulin secretion, GLP-1(9-36)amide has only weak partial insulinotropic agonist activities on the GLP-1 receptor, but suppresses hepatic glucose production, exerts antioxidant cardioprotective actions and reduces oxidative stress in vasculature tissues. These insulin-like activities suggest a role for GLP-1 (9-36)amide in the modulation of mitochondrial functions by mechanisms independent of the GLP-1 receptor. In this paper, we discuss the current literature suggesting that GLP-1(9-36)amide is an active peptide with important insulin-like actions. These findings have implications in nutrient assimilation, energy homeostasis, obesity, and the use of Dpp4 inhibitors for the treatment of diabetes.
Copyright (c) 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Kieffer TJ, Habener JF. The glucagon-like peptides. Endocr Rev. 1999;20:876–913. - PubMed
-
- Estall JL, Drucker DJ. Glucagon-like Peptide-2. Annu Rev Nutr. 2006;26:391–411. - PubMed
-
- Jiang G, Zhang BB. Glucagon and regulation of glucose metabolism. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2003;284:E671–678. - PubMed
-
- Lovshin JA, Drucker DJ. Incretin-based therapies for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2009;5:262–269. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

