Granzyme A- and B-cluster deficiency delays acute lung injury in pneumovirus-infected mice
- PMID: 20018616
- PMCID: PMC2803336
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0903029
Granzyme A- and B-cluster deficiency delays acute lung injury in pneumovirus-infected mice
Abstract
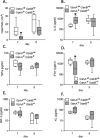
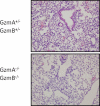
Lower respiratory tract infection by the human pneumovirus respiratory syncytial virus is a frequent cause of acute lung injury in children. Severe pneumovirus disease in humans is associated with activation of the granzyme pathway by effector lymphocytes, which may promote pathology by exaggerating proapoptotic caspase activity and proinflammatory activity. The main goal of this study was to determine whether granzymes contribute to the development of acute lung injury in pneumovirus-infected mice. Granzyme-expressing mice and granzyme A- and B-cluster single- and double-knockout mice were inoculated with the rodent pneumovirus pneumonia virus of mice strain J3666, and were studied for markers of lung inflammation and injury. Expression of granzyme A and B is detected in effector lymphocytes in mouse lungs in response to pneumovirus infection. Mice deficient for granzyme A and the granzyme B cluster have unchanged virus titers in the lungs but show a significantly delayed clinical response to fatal pneumovirus infection, a feature that is associated with delayed neutrophil recruitment, diminished activation of caspase-3, and reduced lung permeability. We conclude that granzyme A- and B-cluster deficiency delays the acute progression of pneumovirus disease by reducing alveolar injury.
Figures
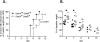
Similar articles
-
The caspase inhibitor zVAD increases lung inflammation in pneumovirus infection in mice.Physiol Rep. 2015 Mar;3(3):e12332. doi: 10.14814/phy2.12332. Physiol Rep. 2015. PMID: 25780096 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanical ventilation enhances lung inflammation and caspase activity in a model of mouse pneumovirus infection.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009 Jan;296(1):L46-56. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00467.2007. Epub 2008 Nov 7. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009. PMID: 18996903 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac dysfunction in pneumovirus-induced lung injury in mice.Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2013 Jun;14(5):e243-9. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0b013e31828a7f9b. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2013. PMID: 23867445
-
Animal models for studying respiratory syncytial virus infection and its long term effects on lung function.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2004 Nov;23(11 Suppl):S228-34. doi: 10.1097/01.inf.0000144672.81955.a4. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2004. PMID: 15577578 Review.
-
Pneumonia virus of mice: severe respiratory infection in a natural host.Immunol Lett. 2008 Jun 15;118(1):6-12. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2008.03.013. Epub 2008 Apr 22. Immunol Lett. 2008. PMID: 18471897 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The caspase inhibitor zVAD increases lung inflammation in pneumovirus infection in mice.Physiol Rep. 2015 Mar;3(3):e12332. doi: 10.14814/phy2.12332. Physiol Rep. 2015. PMID: 25780096 Free PMC article.
-
Pneumovirus-Induced Lung Disease in Mice Is Independent of Neutrophil-Driven Inflammation.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 22;11(12):e0168779. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0168779. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 28005954 Free PMC article.
-
Recent insights into pulmonary repair following virus-induced inflammation of the respiratory tract.Curr Opin Virol. 2012 Jun;2(3):233-41. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2012.04.006. Epub 2012 May 17. Curr Opin Virol. 2012. PMID: 22608464 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In situ evolution of virus-specific cytotoxic T cell responses in the lung.J Virol. 2013 Oct;87(20):11267-75. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00255-13. Epub 2013 Aug 14. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23946463 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Term Pulmonary Dysfunction by Hyperoxia Exposure during Severe Viral Lower Respiratory Tract Infection in Mice.Pathogens. 2022 Nov 12;11(11):1334. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11111334. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 36422586 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shay DK, Holman RC, Newman RD, Liu LL, Stout JW, Anderson LJ. Bronchiolitis-associated hospitalizations among US children, 1980–1996. JAMA. 1999;282:1440–1446. - PubMed
-
- Dahlem P, van Aalderen WM, Hamaker ME, Dijkgraaf MG, Bos AP. Incidence and short-term outcome of acute lung injury in mechanically ventilated children. Eur. Respir. J. 2003;22:980–985. - PubMed
-
- Nokes JD, Cane PA. New strategies for control of respiratory syncytial virus infection. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2008;21:639–643. - PubMed
-
- Ware LB, Matthay MA. The acute respiratory distress syndrome. N. Engl. J Med. 2000;342:1334–1349. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

