Beta-arrestin- but not G protein-mediated signaling by the "decoy" receptor CXCR7
- PMID: 20018651
- PMCID: PMC2818968
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0912852107
Beta-arrestin- but not G protein-mediated signaling by the "decoy" receptor CXCR7
Abstract
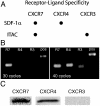
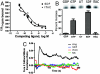
Ubiquitously expressed seven-transmembrane receptors (7TMRs) classically signal through heterotrimeric G proteins and are commonly referred to as G protein-coupled receptors. It is now recognized that 7TMRs also signal through beta-arrestins, which act as versatile adapters controlling receptor signaling, desensitization, and trafficking. Most endogenous receptors appear to signal in a balanced fashion using both beta-arrestin and G protein-mediated pathways. Some 7TMRs are thought to be nonsignaling "decoys" because of their inability to activate typical G protein signaling pathways; it has been proposed that these receptors act to scavenge ligands or function as coreceptors. Here we demonstrate that ligand binding to the decoy receptor CXCR7 does not result in activation of signaling pathways typical of G proteins but does activate MAP kinases through beta-arrestins in transiently transfected cells. Furthermore, we observe that vascular smooth muscle cells that endogenously express CXCR7 migrate to its ligand interferon-inducible T-cell alpha chemoattractant (ITAC), an effect that is significantly attenuated by treatment with either a CXCR7 antagonist or beta-arrestin depletion by siRNA. This example of an endogenous "beta-arrestin-biased" 7TMR that signals through beta-arrestin in the absence of G protein activation demonstrates that some 7TMRs encoded in the genome have evolved to signal through beta-arrestin exclusively and suggests that other receptors that are currently thought to be orphans or decoys may also signal through such nonclassical pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
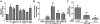
Similar articles
-
Chemokine CXCL12 activates dual CXCR4 and CXCR7-mediated signaling pathways in pancreatic cancer cells.J Transl Med. 2012 Apr 2;10:68. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-10-68. J Transl Med. 2012. PMID: 22472349 Free PMC article.
-
Different G protein-coupled receptor kinases govern G protein and beta-arrestin-mediated signaling of V2 vasopressin receptor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Feb 1;102(5):1448-53. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0409534102. Epub 2005 Jan 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15671180 Free PMC article.
-
Competing G protein-coupled receptor kinases balance G protein and β-arrestin signaling.Mol Syst Biol. 2012 Jun 26;8:590. doi: 10.1038/msb.2012.22. Mol Syst Biol. 2012. PMID: 22735336 Free PMC article.
-
Seven-transmembrane receptor signaling through beta-arrestin.Sci STKE. 2005 Nov 1;2005(308):cm10. doi: 10.1126/stke.2005/308/cm10. Sci STKE. 2005. PMID: 16267056 Review.
-
GRKs and beta-arrestins: roles in receptor silencing, trafficking and signaling.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2006 May-Jun;17(4):159-65. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2006.03.008. Epub 2006 Apr 3. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2006. PMID: 16595179 Review.
Cited by
-
CXCR7 Mediates Neural Progenitor Cells Migration to CXCL12 Independent of CXCR4.Stem Cells. 2015 Aug;33(8):2574-85. doi: 10.1002/stem.2022. Epub 2015 May 13. Stem Cells. 2015. PMID: 25833331 Free PMC article.
-
GPR182 is an endothelium-specific atypical chemokine receptor that maintains hematopoietic stem cell homeostasis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Apr 27;118(17):e2021596118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2021596118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33875597 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetics of CXCL12 binding to atypical chemokine receptor 3 reveal a role for the receptor N terminus in chemokine binding.Sci Signal. 2019 Sep 10;12(598):eaaw3657. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aaw3657. Sci Signal. 2019. PMID: 31506383 Free PMC article.
-
The Emerging Role of Gβ Subunits in Human Genetic Diseases.Cells. 2019 Dec 4;8(12):1567. doi: 10.3390/cells8121567. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31817184 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Atypical Roles of the Chemokine Receptor ACKR3/CXCR7 in Platelet Pathophysiology.Cells. 2022 Jan 9;11(2):213. doi: 10.3390/cells11020213. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35053329 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ma P, Zemmel R. Value of novelty? Nat Rev Drug Discovery. 2002;1(8):571–572. - PubMed
-
- Lefkowitz RJ, Shenoy SK. Transduction of receptor signals by beta-arrestins. Science. 2005;308(5721):512–517. - PubMed
-
- Benovic JL, Staniszewski C, Mayor F, Jr., Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ. beta-Adrenergic receptor kinase. Activity of partial agonists for stimulation of adenylate cyclase correlates with ability to promote receptor phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1988;263(8):3893–3897. - PubMed
-
- Kenakin T. Collateral efficacy in drug discovery: taking advantage of the good (allosteric) nature of 7TM receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2007;28(8):407–415. - PubMed
-
- Gesty-Palmer D, et al. Distinct beta-arrestin- and G-protein-dependent pathways for parathyroid hormone receptor-stimulated ERK1/2 activation. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(16):10856–10864. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

