Chloroplast acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity is 2-oxoglutarate-regulated by interaction of PII with the biotin carboxyl carrier subunit
- PMID: 20018655
- PMCID: PMC2806706
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0910097107
Chloroplast acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity is 2-oxoglutarate-regulated by interaction of PII with the biotin carboxyl carrier subunit
Abstract
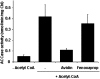
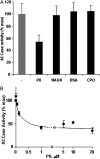
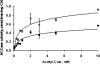
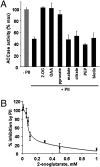
The PII protein is a signal integrator involved in the regulation of nitrogen metabolism in bacteria and plants. Upon sensing of cellular carbon and energy availability, PII conveys the signal by interacting with target proteins, thereby modulating their biological activity. Plant PII is located to plastids; therefore, to identify new PII target proteins, PII-affinity chromatography of soluble extracts from Arabidopsis leaf chloroplasts was performed. Several proteins were retained only when Mg-ATP was present in the binding medium and they were specifically released from the resin by application of a 2-oxoglutarate-containing elution buffer. Mass spectroscopy of SDS/PAGE-resolved protein bands identified the biotin carboxyl carrier protein subunits of the plastidial acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACCase) and three other proteins containing a similar biotin/lipoyl-binding motif as putative PII targets. ACCase is a key enzyme initiating the synthesis of fatty acids in plastids. In in vitro reconstituted assays supplemented with exogenous ATP, recombinant Arabidopsis PII inhibited chloroplastic ACCase activity, and this was completely reversed in the presence of 2-oxoglutarate, pyruvate, or oxaloacetate. The inhibitory effect was PII-dose-dependent and appeared to be PII-specific because ACCase activity was not altered in the presence of other tested proteins. PII decreased the V(max) of the ACCase reaction without altering the K(m) for acetyl-CoA. These data show that PII function has evolved between bacterial and plant systems to control the carbon metabolism pathway of fatty acid synthesis in plastids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ninfa AJ, Jing P. PII signal transduction proteins: sensors of α-ketoglutarate that regulate nitrogen metabolism. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2005;8:168–173. - PubMed
-
- Forchhammer K. Global carbon/nitrogen control by PII signal transduction in cyanobacteria: from signals to targets. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2004;28:319–333. - PubMed
-
- Osanai T, Tanika K. Keeping in touch with PII: PII-interacting proteins in unicellular cyanobacteria. Plant Cell Physiol. 2007;48:908–914. - PubMed
-
- Forchhammer K. PII signal transducers: novel functional and structural insights. Trends Microbiol. 2008;16:65–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

