Identification of a small-molecule inhibitor of the PICK1 PDZ domain that inhibits hippocampal LTP and LTD
- PMID: 20018661
- PMCID: PMC2806717
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0902225107
Identification of a small-molecule inhibitor of the PICK1 PDZ domain that inhibits hippocampal LTP and LTD
Abstract
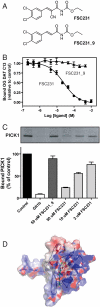
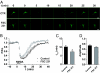
Proteins containing PSD-95/Discs-large/ZO-1 homology (PDZ) domains play key roles in the assembly and regulation of cellular signaling pathways and represent putative targets for new pharmacotherapeutics. Here we describe the first small-molecule inhibitor (FSC231) of the PDZ domain in protein interacting with C kinase 1 (PICK1) identified by a screening of approximately 44,000 compounds in a fluorescent polarization assay. The inhibitor bound the PICK1 PDZ domain with an affinity similar to that observed for endogenous peptide ligands (K(i) approximately 10.1 microM). Mutational analysis, together with computational docking of the compound in simulations starting from the PDZ domain structure, identified the binding mode of FSC231. The specificity of FSC231 for the PICK1 PDZ domain was supported by the lack of binding to PDZ domains of postsynaptic density protein 95 (PSD-95) and glutamate receptor interacting protein 1 (GRIP1). Pretreatment of cultured hippocampal neurons with FSC231 inhibited coimmunopreciptation of the AMPA receptor GluR2 subunit with PICK1. In agreement with inhibiting the role of PICK1 in GluR2 trafficking, FSC231 accelerated recycling of pHluorin-tagged GluR2 in hippocampal neurons after internalization in response to NMDA receptor activation. FSC231 blocked the expression of both long-term depression and long-term potentiation in hippocampal CA1 neurons from acute slices, consistent with inhibition of the bidirectional function of PICK1 in synaptic plasticity. Given the proposed role of the PICK1/AMPA receptor interaction in neuropathic pain, excitotoxicity, and cocaine addiction, FSC231 might serve as a lead in the future development of new therapeutics against these conditions.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: T.S.T., K.L.M., T.D., D.P., L.C.B.R., and U.G. have filed a patent application for FSC231.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Lipid binding regulates synaptic targeting of PICK1, AMPA receptor trafficking, and synaptic plasticity.J Neurosci. 2006 Mar 1;26(9):2380-90. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3503-05.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16510715 Free PMC article.
-
An essential role for PICK1 in NMDA receptor-dependent bidirectional synaptic plasticity.Neuron. 2008 Mar 27;57(6):872-82. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.01.028. Neuron. 2008. PMID: 18367088 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of the AMPA receptor subunit GluR2 differentially regulates its interaction with PDZ domain-containing proteins.J Neurosci. 2000 Oct 1;20(19):7258-67. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-19-07258.2000. J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 11007883 Free PMC article.
-
Protein interacting with C kinase and neurological disorders.Synapse. 2013 Aug;67(8):532-40. doi: 10.1002/syn.21657. Epub 2013 Mar 20. Synapse. 2013. PMID: 23436724 Review.
-
Multiple faces of protein interacting with C kinase 1 (PICK1): Structure, function, and diseases.Neurochem Int. 2016 Sep;98:115-21. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2016.03.001. Epub 2016 Mar 9. Neurochem Int. 2016. PMID: 26970394 Review.
Cited by
-
Computational Analysis of Energy Landscapes Reveals Dynamic Features That Contribute to Binding of Inhibitors to CFTR-Associated Ligand.J Phys Chem B. 2019 Dec 12;123(49):10441-10455. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.9b07278. Epub 2019 Nov 27. J Phys Chem B. 2019. PMID: 31697075 Free PMC article.
-
Peptide Targeting of PDZ-Dependent Interactions as Pharmacological Intervention in Immune-Related Diseases.Molecules. 2021 Oct 21;26(21):6367. doi: 10.3390/molecules26216367. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34770776 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Themes in PDZ Domain Signaling: Structure, Function, and Inhibition.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2019;343:129-218. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2018.05.013. Epub 2018 Jun 28. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30712672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An in silico analysis of the binding modes and binding affinities of small molecule modulators of PDZ-peptide interactions.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 8;8(8):e71340. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071340. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23951139 Free PMC article.
-
KIF14 negatively regulates Rap1a-Radil signaling during breast cancer progression.J Cell Biol. 2012 Dec 10;199(6):951-67. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201206051. Epub 2012 Dec 3. J Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 23209302 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aarts M, et al. Treatment of ischemic brain damage by perturbing NMDA receptor-PSD-95 protein interactions. Science. 2002;298:846–850. - PubMed
-
- Arkin MR, Wells JA. Small-molecule inhibitors of protein-protein interactions: progressing towards the dream. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2004;3:301–317. - PubMed
-
- Wells JA, McClendon CL. Reaching for high-hanging fruit in drug discovery at protein-protein interfaces. Nature. 2007;450:1001–1009. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

