PGC-1alpha negatively regulates hepatic FGF21 expression by modulating the heme/Rev-Erb(alpha) axis
- PMID: 20018698
- PMCID: PMC2799738
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0912533106
PGC-1alpha negatively regulates hepatic FGF21 expression by modulating the heme/Rev-Erb(alpha) axis
Abstract
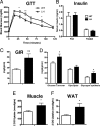
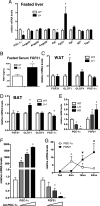
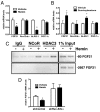
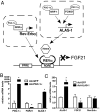
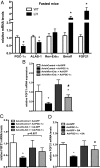
FGF21 is a hormone produced in liver and fat that dramatically improves peripheral insulin sensitivity and lipid metabolism. We show here that obese mice with genetically reduced levels of a key hepatic transcriptional coactivator, PGC-1alpha, have improved whole-body insulin sensitivity with increased levels of hepatic and circulating FGF21. Gain- and loss-of-function studies in primary mouse hepatocytes show that hepatic FGF21 levels are regulated by the expression of PGC-1alpha. Importantly, PGC-1alpha-mediated reduction of FGF21 expression is dependent on Rev-Erbalpha and the expression of ALAS-1. ALAS-1 is a PGC-1alpha target gene and the rate-limiting enzyme in the synthesis of heme, a ligand for Rev-Erbalpha. Modulation of intracellular heme levels mimics the effect of PGC-1alpha on FGF21 expression, and inhibition of heme biosynthesis completely abrogates the down-regulation of FGF21 in response to PGC-1alpha. Thus, PGC-1alpha can impact hepatic and systemic metabolism by regulating the levels of a nuclear receptor ligand.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
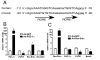
References
-
- Lin J, Handschin C, Spiegelman BM. Metabolic control through the PGC-1 family of transcription coactivators. Cell Metab. 2005;1:361–370. - PubMed
-
- Liu C, Li S, Liu T, Borjigin J, Lin JD. Transcriptional coactivator PGC-1α integrates the mammalian clock and energy metabolism. Nature. 2007;447:477–481. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

