Identification and characterization of Bph14, a gene conferring resistance to brown planthopper in rice
- PMID: 20018701
- PMCID: PMC2793316
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0912139106
Identification and characterization of Bph14, a gene conferring resistance to brown planthopper in rice
Abstract
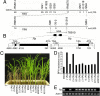
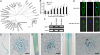
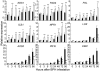
Planthoppers are highly destructive pests in crop production worldwide. Brown planthopper (BPH) causes the most serious damage of the rice crop globally among all rice pests. Growing resistant varieties is the most effective and environment-friendly strategy for protecting the crop from BPH. More than 19 BPH-resistance genes have been reported and used to various extents in rice breeding and production. In this study, we cloned Bph14, a gene conferring resistance to BPH at seedling and maturity stages of the rice plant, using a map-base cloning approach. We show that Bph14 encodes a coiled-coil, nucleotide-binding, and leucine-rich repeat (CC-NB-LRR) protein. Sequence comparison indicates that Bph14 carries a unique LRR domain that might function in recognition of the BPH insect invasion and activating the defense response. Bph14 is predominantly expressed in vascular bundles, the site of BPH feeding. Expression of Bph14 activates the salicylic acid signaling pathway and induces callose deposition in phloem cells and trypsin inhibitor production after planthopper infestation, thus reducing the feeding, growth rate, and longevity of the BPH insects. Our work provides insights into the molecular mechanisms of rice defense against insects and facilitates the development of resistant varieties to control this devastating insect.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Coiled-Coil and Nucleotide Binding Domains of BROWN PLANTHOPPER RESISTANCE14 Function in Signaling and Resistance against Planthopper in Rice.Plant Cell. 2017 Dec;29(12):3157-3185. doi: 10.1105/tpc.17.00263. Epub 2017 Nov 1. Plant Cell. 2017. PMID: 29093216 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the structure-function relationship of brown plant hopper resistance protein, Bph14 of rice plant: a computational structural biology approach.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2019 Apr;37(7):1649-1665. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2018.1462737. Epub 2018 May 2. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2019. PMID: 29633905
-
Recent Advances in Gene Mining and Hormonal Mechanism for Brown Planthopper Resistance in Rice.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 2;25(23):12965. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312965. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Towards understanding of molecular interactions between rice and the brown planthopper.Mol Plant. 2013 May;6(3):621-34. doi: 10.1093/mp/sst030. Epub 2013 Feb 9. Mol Plant. 2013. PMID: 23396040 Review.
-
An R2R3 MYB transcription factor confers brown planthopper resistance by regulating the phenylalanine ammonia-lyase pathway in rice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Jan 7;117(1):271-277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1902771116. Epub 2019 Dec 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 31848246 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comparative iTRAQ proteomic profiling of proteins associated with the adaptation of brown planthopper to moderately resistant vs. susceptible rice varieties.PLoS One. 2020 Sep 9;15(9):e0238549. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0238549. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32903256 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Oryza sativa L. by Oryza punctata Kotschy ex Steud. monosomic addition lines with high value traits by interspecific hybridization.Theor Appl Genet. 2016 Oct;129(10):1873-86. doi: 10.1007/s00122-016-2745-8. Epub 2016 Jun 18. Theor Appl Genet. 2016. PMID: 27318700
-
A Group D MAPK Protects Plants from Autotoxicity by Suppressing Herbivore-Induced Defense Signaling.Plant Physiol. 2019 Apr;179(4):1386-1401. doi: 10.1104/pp.18.01411. Epub 2019 Jan 2. Plant Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30602493 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a drought stress-resistant rice restorer line through Oryza sativa-rufipogon hybridization.J Genet. 2019 Jun;98(2):55. J Genet. 2019. PMID: 31204722
-
The Desaturase Gene Nlug-desatA2 Regulates the Performance of the Brown Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens and Its Relationship with Rice.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 10;21(11):4143. doi: 10.3390/ijms21114143. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32532001 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Normile D. Reinventing rice to feed the world. Science. 2008;321:330–333. 7. - PubMed
-
- Sōgawa K. The rice brown planthopper: Feeding physiology and host plant interactions. Annu Rev Entomol. 1982;27:49–73.
-
- Du PV, et al. Yellowing syndrome of rice: Etiology, current status and future challenges. Omonrice. 2007;15:94–101.
-
- Tanaka K, Endo S, Kazano H. Toxicity of insecticides to predators of rice planthoppers: Spiders, the mirid bug and the dryinid wasp. Appl Entomol Zool. 2000;35:177–187.
-
- Khush GS. Green revolution: The way forward. Nat Rev Genet. 2001;2:815–822. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

